Faraday's Law of Electromagnetic Induction
Faraday's Law of Electromagnetic Induction: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Magnetic Flux, Magnetic Flux for Constant Magnetic Field, Magnetic Flux for Variable Magnetic Field, Faraday's Laws of Electromagnetic Induction & Electromagnetic Induction etc.
Important Questions on Faraday's Law of Electromagnetic Induction
The magnetic flux through each of five faces of a neutral playing dice is given , where N (= 1 to 5) is the number of spots on the face. The flux is positive (out-ward) for N even and negative (inward) for N odd. What is the flux through the sixth face of the die?
According to Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction:
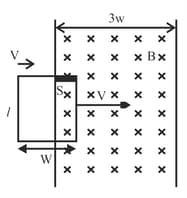
A rectangular loop and a circular loop are moving out of a uniform magnetic field to a field – free region with a constant velocity ‘v’ as shown in the figure. Explain which loop do you expect the induced emf to be constant during the passage out of the field region. The magnetic field is normal to the loops.
(i) In an a.c. generator, coil of turns and area is rotated at revolution per second in a uniform magnetic field . Write the expression for the emf produced.
(ii) A turn coil of area rotates at half a revolution per second. It is placed in a magnetic field perpendicular to the axis of rotation of the coil. Calculate the maximum voltage generated in the coil.
The dimensional formula of magnetic flux is
A circular coil of one turn of radius is rotated about a diameter with a constant angular speed of revolutions per minute. A uniform magnetic field exists in a direction perpendicular to the axis of rotation. Find the average of the square of emf induced in the coil over one time period
A rectangular coil of two turns having arearotates in a uniform magnetic field with angular speed about an axis perpendicular to the field and in plane of the coil. If initially the plane of the coil is perpendicular to the field, then the average induced emf when it has rotated through is is
Through a long solenoid of diameter , having turns per , a current is flowing. At its centre, a turns closely packed coil of diameter is placed such that the coil is co-axial with the long solenoid. The current in the solenoid is reduced to zero at a steady rate in . What is the magnitude of emf induced (in ) in the coil while the current in the solenoid is changing?
In a coil of resistance , the magnetic flux due to an external magnetic field varies with time as . The value of total heat produced (in ) till the flux becomes zero will be:
A rectangular loop of dimensions & and resistance moves with constant velocity to the right as shown in the figure. It continues to move with same speed through a region containing a uniform magnetic field directed into the plane of the paper & extending a distance . Sketch the flux, induced emf & external force acting on the loop as a function of the distance.
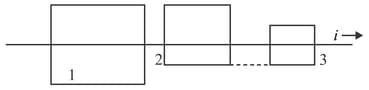
A long straight wire with current passes (without touching) three square wire loops with edge lengths land . The loops are widely spaced (so as to not affect one another). Loops 1 and 3 are symmetric about the long wire. Rank the loops according to the size of the current induced in them if current is (a) constant and (b) increasing greatest first.

Find the magnitude of magnetic flux through the circular loop at
A circular loop of radius is placed in a uniform magnetic field Tesla as shown. Which of the following is incorrect?
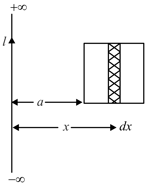
Figure shows a long straight wire carrying current and a square conducting wire loop of side , at a distance '' from current wire. Both the current wire and loop are in the plane of paper.Find the flux of magnetic field of current wire, passing through the loop.
Why magnetic flux is minimum when angle between magnetic field and area is and why not it is minimum when angle between magnetic flux and area is ?
A wire, bent into the shape of a right angled triangle , lies with its side parallel to a current carrying wire, and side perpendicular to it. The loop lies in the plane of the wire. EMF induced in the loop when it is moved with constant speed along is and it is when moved along with the same constant speed. Then,
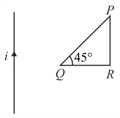
The radius of a circular coil changes with time as shown in the figure. If it is kept in an uniform magnetic field, then choose the correct graph which plots the variation of the magnitude of the emf induced with the time in the coil.
If a copper wire of length and diameter is bent into a circular loop and placed perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field that is increasing at a constant rate of What will be the rate at which the thermal energy (in ) is generated in the loop?
[Given: Resistivity of copper ]
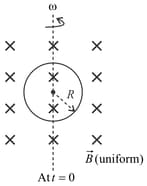
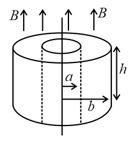
A conducting ring of circular cross-section with inner and outer radii and is made out of a material of resistivity . The thickness of the ring is . It is placed coaxially in a vertical cylindrical region of a magnetic field , where is a positive constant, is the distance from the axis and is the time. If the current through the ring is , then what is the value of ?
A circuit consists of a coil with inductance and an uncharged capacitor of capacitance . The coil is in a constant uniform magnetic field such that the flux through the coil is . At time , the magnetic field is abruptly switched OFF. Let and ignore the resistance of the circuit. Then,
