Induced Electric Field
Induced Electric Field: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Induced Electric Field, Induced Electric Field Due to Time Variable Magnetic Field in Cylindrical Region, and Properties of Induced Electric Field.
Important Questions on Induced Electric Field
A thin non-conducting ring of mass and radius currying a charge can rotate freely about its own axis which is vertical. At the initial moment the ring was at rest in horizontal position and no magnetic field was present. At instant , a uniform magnetic field is switched on which is vertically downward and increases with time according to the law . Neglecting magnetism induced due to rotational motion of ring.
Angular acceleration of the ring is:
The circular wire in figure below encircles solenoid in which the magnetic flux is increasing at a constant rate out of the plane of the page.
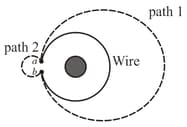
The clockwise emf around the circular loop is By definition a voltammeter measures the voltage difference between the two points given
by We assume that and are infinitesimally close to each other. The values of along the path and along the path respectively are
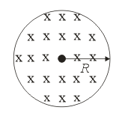
As shown in the above figure, there is a uniform magnetic induction parallel to the axis of a cylindrical space of radius . Plot the graph between the induced electric field and distance from the axis of the cylinder, if it is known that the rate of change of magnetic induction is constant.
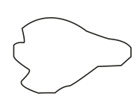
As shown in the above figure, consider a closed-loop held in a magnetic field. The change in the magnetic flux linked with the loop induces a voltage in the loop. Now, find the work done in taking a charge over a complete loop:
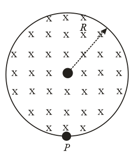
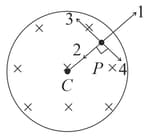
Consider a cylindrical region of radius , where a uniform magnetic field of induction is confined. At point , a negative charge of magnitude is placed. Find the acceleration of the charge, if , where is a constant.
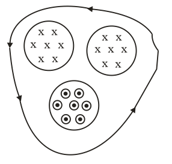
As shown in the above figure, a loop surrounds three regions of the magnetic field where the magnitude of the magnetic field is decreasing at a constant rate . Take the area of each region as . Now find the along the given loop, where is the induced electric field.
Consider the uniform magnetic field of magnitude directed perpendicularly to the plane of a conducting ring of the radius . If the ring is oscillating with a frequency of , then find the induced electric field.
A thin non-conducting ring of mass and radius carrying a charge can rotate freely about its own axis which is vertical. At the initial moment the ring was at rest in horizontal position and no magnetic field was present. At instant , a uniform magnetic field is switched on which is vertically downward and increases with time according to the law . Neglecting magnetism induced due to rotational motion of ring.
Angular acceleration of the ring is:
A massless non-conducting rod of length is placed in uniform time varying magnetic field confined in a cylindrical regions of radius as shown in the figure. The centre of the rod coincides with the centre of the cylindrical region. The rod can freely rotate in the plane of the figure about an axis coinciding with the axis of the cylinder. Two particles, each of mass and charge are attached to the ends and of the rod. The time varying magnetic field in this cylindrical region is given by where is a constant. The field is switched on at time . Consider: . Calculate the time (in ) in which the rod will reach position shown in the figure for the first time.
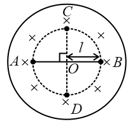
A thin non-conducting ring of mass , radius carrying a charge can rotate freely about its own axis which is vertical. At the initial moment, the ring was at rest in horizontal position and no magnetic field was present. At instant , a uniform magnetic field is switched on which is vertically downward and increase with time according to the law . Neglecting magnetism induced due to rotational motion of ring.
If the surface of a ring is perpendicular to Magnetic Field, then the magnitude of an electric field on the circumference of the ring is: (Take and as the magnetic field and the radius of ring)A uniform magnetic field of induction is confined in a cylindrical region of the radius . If the field is increasing at a constant rate of , then the intensity of the electric field induced at a point distant from the axis as shown in the figure is equal to
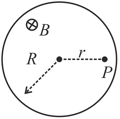
A conductor is moving with velocity v in a region of uniform magnetic field B. The electric field at P inside conductor is
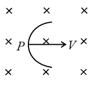
A uniform but time varying magnetic field exists in cylindrical region and directed into the paper. If field decreases with time and a positive charge is placed at any point inside the region, then it moves
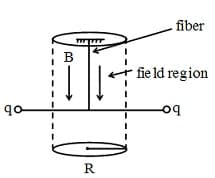
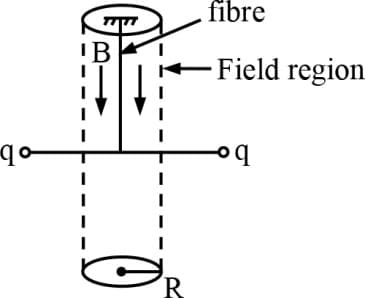
Two small pith balls, each carrying a charge are attached to the ends of a light rod of length , which is suspended from the ceiling by a thin torsion-free fiber as shown in the figure. There is a uniform magnetic field pointing straight down, in the cylindrical region of radius around the fiber. The system is initially at rest. If the magnetic field is turned off, which of the following happens to the system?
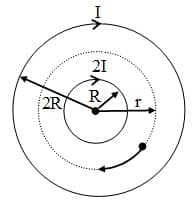
A long solenoid contains another coaxial solenoid (whose radius is half of its own). Their coils have the same number of turns per unit length and initially both carry no current. At the same instant, currents start increasing linearly with time in both solenoids. At any moment, the current flowing in the inner coil is twice as large as that in the outer one and their directions are the same. As a result of the increasing currents, a charged particle, initially at rest between the solenoids, starts moving along a circular trajectory (see figure). What is the radius of the circle ?
A uniform but time-varying magnetic field exists in the cylindrical region and directed into the paper. If field decrease with time and a positive charge placed at any point inside the region, then it moves
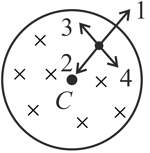
Two small pith balls, each carrying a charge are attached to the ends of a light rod of length , which is suspended from the ceiling by a thin torsion free fibre as shown in figure. There is a uniform magnetic field pointing straight down, in the cylindrical region of radius around the fibre. The system is initially at rest. If the magnetic field is turned off, which of the following happen to the system -
As a result of change in magnetic flux linked with the closed loop shown in the figure, an emf is induced in the loop. The work done in taking a charge, , once along the loop is,
A conducting ring of radius is placed in a uniform magnetic field , of oscillating with frequency with its plane at right angles to . What will be the induced electric field?
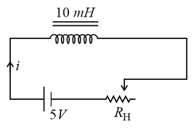
The resistance in the following circuit is increased at a particular instant. At this instant the value of resistance is . The current in the circuit will be now