Motional Electromotive Force
Motional Electromotive Force: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Motional Emf in a Conductor, Fleming's Right Hand Rule for Induced Current, Derivation of Motional Emf, Motional Emf in a Rotating Conducting Rod & Charge Flown in Changing Magnetic Flux etc.
Important Questions on Motional Electromotive Force
A jet plane is travelling towards wets at a speed of . What is the voltage difference developed between the ends of the wing having a span of , if the Earth’s magnetic field at the location has a magnitude of and the dip angle is ?
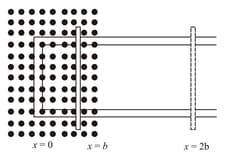
Figure shows a rectangular conductor in which the conductor is free to move in a uniform magnetic field perpendicular to the plane of the paper. The field extends from to and is zero for . Assume that only the arm possesses resistance . When the arm is pulled outward from with constant speed , the joules heating loss from would be:
The figure given below shows an arrangement by which current flows through the bulb (X) connected with coil B, when a.c. is passed through coil A.
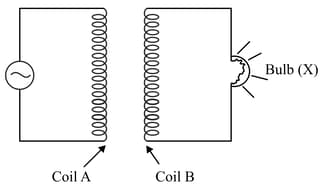
(i) Name the phenomenon involved.
(ii) If a copper sheet is inserted in the gap between the coils, explain how the brightness of the bulb would change.
A conducting of length and mass is rotating about point with angular momentum A uniform magnetic field is directed into the paper. Given, and Then, is times . What is the value of ?

A conducting rod of length is moving with a uniform speed in a uniform magnetic field of which is directed into the paper. A capacitor of capacity is connected as shown in the figure. Then the charges on the plates of the capacitor are

A loop is moving with velocity towards right. The magnetic field is . Loop is connected to a resistance of . If steady current of flows in the loop, then value of , if loop has resistance of is (given, )

The total charge induced in a conducting loop, when it is moved in magnetic field depends on
A conducting rod of length is moving with a uniform speed on conducting rails in a magnetic field as shown. On one side, the end of the rails is connected to a capacitor of capacitance Then the charges on the capacitor plates are:

A semicircular insulated conductor of radius (lying in plane) is rotated at uniform angular speed of about an axis passing through one of the ends of the conductor (say ) in the presence of an external uniform magnetic field . Both the axis of rotation and the magnetic field are normal to the plane of the semicircle. If the induced voltage between the ends of the conductor is . What is the strength of magnetic field in ?
Two parallel rails of a railways track, insulated from each other and with the ground, are connected to a millivoltmeter. The distance between the rails is one metre. A train is travelling with a velocity of along the track. The reading of the millivotmeter (in ) is (Vertical component of the earth's magnetic induction is,
A copper rod of length is rotated about one end, perpendicular to the magnetic field , with constant angular velocity . The induced emf between the two ends of the rod is,
A solid metal cube of edge length is moving in a positive -direction at a constant speed of . There is a uniform magnetic field of in the positive -direction. The potential difference between the two faces of the cube perpendicular to the -axis, is:
The total charge, induced in a conducting loop, when it is moved in a magnetic field depends on
A cycle wheel with spokes each of length long is rotated at a speed of in a plane normal to the earth's magnetic induction of . Calculate the e.m.f. induced between the (i) axle and the rim of the cycle wheel. (ii) ends of single spoke and ten spokes.
A conducting long wire is placed perpendicular to magnetic field. Wire is moving perpendicular to its length and magnetic field. If wire moves in , then find induced emf between its ends.
A conductor of length is moving with velocity in magnetic field. Find out potential difference across the ends of conductor.
A rectangular loop is moving perpendicular to a non-uniform magnetic field with constant velocity. Find out the expression for induced emf and current and also prove that the law of conservation of energy holds good here.
A conducting wire is moving towards right (with velocity ) in magnetic field . If direction of induced current is as shown in figure then the direction of magnetic field is-
A copper wire coil and a wire are place in the plane of paper as shown in figure. If current in wire increases from to along the direction show in figure, then what is the direction of induced current in coil-

A conducting rod is moving with velocity in a magnetic field . An emf is induced across its ends when-

