Current Carrying Conductor in Magnetic Field
Current Carrying Conductor in Magnetic Field: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Lorentz Force, Force on a Straight Current Wire in Uniform Magnetic Field, Force between Two Parallel Current Wires, One Ampere Electric Current, Direction of Magnetic Force on a Current Carrying Wire, etc.
Important Questions on Current Carrying Conductor in Magnetic Field
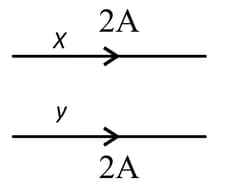
In given figure, X and Y are two long straight parallel conductors each carrying a current of 2 A. The force on each conductor is F newtons. When the current in each is changed to 1 A and reversed in direction, the force on each is now
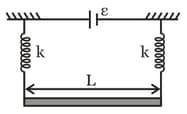
A straight rod of mass m and length is suspended from the identical spring as shown in the figure. The spring stretched by a distance of due to the weight of the wire. The circuit has total resistance . When the magnetic field perpendicular to the plane of the paper is switched on, springs are observed to extend further by the same distance. The magnetic field strength is
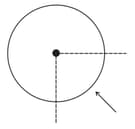
A long thin-walled pipe of radius carries a current along its length. The current density is uniform over the circumference of the pipe. The magnetic field at the centre of the pipe due to the quarter portion of the pipe shown, is
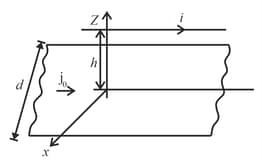
An infinite wire placed along -axis, has current in positive -direction. A conducting rod placed in plane parallel to y-axis has current in positive y-direction. The ends of the rod subtend angles of and at the origin with positive -direction. The rod is at a distance from the origin. Find net force on the rod.
A conductor wire carrying current is placed symmetrically and parallel to a long conducting sheet having a current per unit width and width , as shown in the figure. the force per unit length on the conductor wire will be
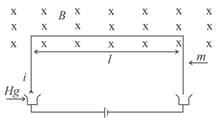
A shaped wire of mass and length is immersed with its two ends in mercury (see figure). The wire is in a homogeneous field of magnetic induction . If a charge, that is, a current pulse sent through the wire, the wire will jump up. Calculate, from the height that the wire reaches, the size of the charge or current pulse, assuming that the time of the current pulse is very small in comparison with the time of flight. Make use of the fact that impulse of force equals which equals . Evaluate for following details:
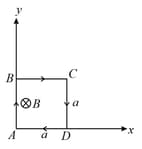
A rectangular loop of wire is oriented with the left corner at the origin, one edge along X-axis and the other edge along Y-axis as shown figure. A magnetic field is into the page and has a magnitude that is given by b=constant. Find the total magnetic force on the loop if it carries current i.
Electric charge is uniformly distributed over a rod of length . The rod is placed parallel to a long wire carrying a current . The separation between the rod and the wire is . Find the force needed to move the rod along its length with a uniform velocity .
A parallel plate capacitor is charged by a battery. After some time the battery is disconnected and a dielectric slab of dielectric constant K is inserted between the plates. How would (i) the capacitance, (ii) the electric field between the plates and (iii) the energy stored in the capacitor, be affected?
Which of the following expressions correctly describes for the force between two long parallel current carrying conductors:
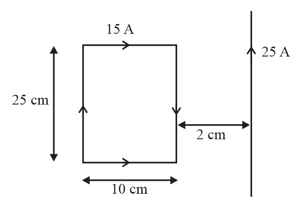
Figure shows a rectangular current-carrying loop placed away from a long, straight, current-carrying conductor. What is the magnitude of the net force acting on the loop in .
What is the expression for the force acting per unit length on one conductor due to the other for two parallel wires.
What is unit of magnetic field?
What SI base unit definitions does the definition of the tesla depend on?
What units are a tesla?
What is the dimension of Tesla?
What is magnetic force in current carrying wires?
Why two wires carrying current in the same direction attract each other?
Why do 2 parallel conductors carrying current exert force on each other?
What is the nature of force between two parallel current?
