Equipotential Surfaces
Equipotential Surfaces: Overview
This topic consists of various concepts like Equipotential Surfaces,Properties of Equipotential Surfaces,Equipotential Surfaces due to a Point Charge, etc.
Important Questions on Equipotential Surfaces
Choose the incorrect statement.
Equipotential surfaces
If a charge is moved around a charge in circular path of radius with as centre then potential difference between any two points on circumference is
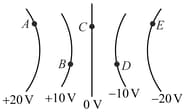
A non-uniform electric field is represented by equipotential lines. What is the direction of the electric field line at point ?
Equipotential spheres are drawn round a point charge. As we move away from the charge, will the spacing between two spheres having a constant potential difference decrease, increase or remain constant.
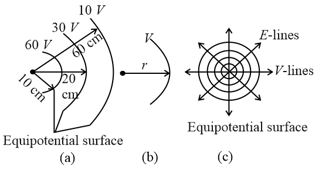
Referring to the spherical equipotential lines in Fig. find
(a) , (b) -pattern.
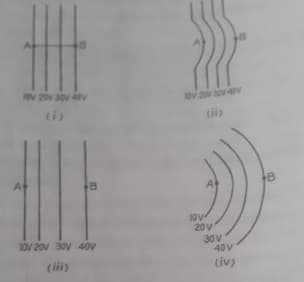
A positive charge q is moved from A to B in each diagram :
Draw the equipotential surface due to a system of two identical positive charges.
Draw the equipotential surface due to a dipole.
What will be the shape of equipotential surface in case of uniform electric field?
The shape of the equipotential surface due to a point charge is:
Assertion: Two equipotential surfaces cannot cut each other.
Reason: Two equipotential surfaces are parallel to each other.
Assertion(A): Electric field is always normal to equipotential surfaces and along the direction of decreasing order of potential.
Reason (R): Negative gradient of electric potential is electric field.
Nature of equipotential surface for a point charge is
What is equipotential surface? Draw the equipotential surface due to point charge.
Draw an equipotential surface in a uniform electric field.
What is the direction of the lines of force at any point on the equipotential surface?
The current following through a pure inductor of inductance is ampere. What is .
The instantaneous values of current and voltage in an circuit are given by . Then
In an ac circuit the current and the A.C. potential is Volt. Then the power consumed is.
Draw the equipotential surfaces due to an electric dipole. Locate the points where the potential due to the dipole is zero.