Potential Due to a Electric Dipole
Potential Due to a Electric Dipole: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Electric Potential Due to Dipole at Axial Point, Electric Potential Due Dipole at Equatorial Point & Electric Potential Due to Dipole at General Point etc.
Important Questions on Potential Due to a Electric Dipole
The electric potential at the equatorial position due to the dipole is zero.
An electric dipole of length having charge placed at with respect to a uniform electric field experiences a torque of magnitude . The potential energy of the dipole is
A molecule of a substance has a permanent electric dipole moment of magnitude . A mole of this substance is polarized by applying a strong electrostatic field of magnitude . The direction of field is changed by an angle . The heat released by the substance in aligning it's dipole along the new direction of the field is:
Which of the following is not true?
Two charges and are placed apart. The electric field at point , on the axis of the dipole away from its centre on the side of the positive charge is
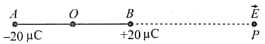
Two electric dipoles and are at points and separate by distance Find the distance from point where net electric potential is zero.
In the given dipole, for , the electric potential at will be
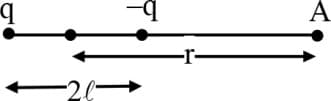
An electric dipole is fixed at the origin of coordinates. Its moment is directed in the positive -direction. A positive charge is moved from the point to the point by an external agent. In this process, the work done by the agent is
A short dipole is placed along -axis with centre at origin. The electric field at a point , which is at a distance from origin such that, makes an angle of with -axis, is directed along a direction making -
Two charges and are kept apart. Then at any point on the right bisector of line joining the two charges,
The ratio of electric field and potential () at mid-point of electric dipole of length , for which separation is
