Capacitance
Capacitance: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Effect of Dielectric on the Value of Capacitance, Parallel Plate Capacitors, Force on the Dielectric inside a Capacitor & Force between Plates of a Charged Parallel Plate Capacitor etc.
Important Questions on Capacitance
The two plates of a parallel plate capacitor are apart. A slab of a dielectric, of thickness is introduced between the plates with its faces parallel to them. The distance between the plates is adjusted so that the capacitance of the capacitor becomes equal to its original value. If the new distance between the plates equal , what is the dielectric constant of the dielectric used?
The two plates of a parallel plate capacitor are apart. A slab of dielectric constant and thickness is introduced between the plates with its faces parallel to them. The distance between the plates is so adjusted that the capacitance of the capacitor becomes of its original value. What is the new distance between the plates?
On charging a parallel plate capacitor to a potential V, the spacing between the plates is halved, and a dielectric medium of is introduced between the plates, without disconnecting the d.c. source. Explain, using suitable expressions, how the
(i) capacitance,
(ii) potential difference and
(iii) energy stored in the capacitor change.
If two similar plates, each of area having surface charge densities are separated by a distance in air, write expressions for the potential difference between the plates.
capacitor is charged by a 100 V supply. The supply is then disconnected and the charged capacitor is connected to another uncharged capacitor. How much electrostatic energy of the first capacitor is lost in the process of attaining the steady situation (in mJ)
A medium having dielectric constant fills the space between the plates of a parallel plate capacitor. The plates have large area, and the distance between them is . The capacitor is connected to a battery of voltage . as shown in Figure (a). Now, both the plates are moved by a distance of from their original positions, as shown in Figure (b).
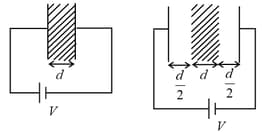
In the process of going from the configuration depicted in Figure (a) to that in Figure (b), which of the following statement(s) is(are) correct?
A parallel plate capacitor with plate area and plate separation is filled with three dialectic slabs. Slabs with dielectric constant and and occupies half space between the plates as shown. Then capacity of the arrangement is
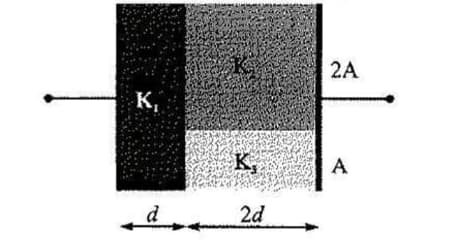
The space between the plates of a parallel plate capacitor is filled completely with a dielectric substance having dielectric constant and thickness . The distance between the plates is now increased by inserting a second sheet of thickness and dielectric constant . If the capacitance of the capacitor so formed is one half of the original capacitance (with dielectric), the value of is . Find ?
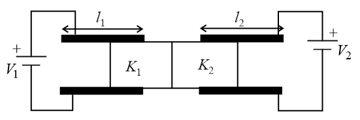
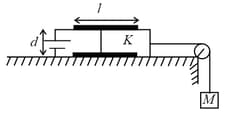
Figure shows two parallel plate capacitors with fixed plates and connected to two batteries. The separation between the plates is the same for the two capacitors. The plates are rectangular in shape with width and length and . The left half of the dielectric slab has a dielectric constant and the right half . Neglecting any friction, find the ratio of the emf of the left battery to that of the right battery for which the dielectric slab may remain in equilibrium.
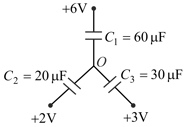
Three uncharged capacitors of capacitance and are connected to one another as shown in figure. If the potential at is then ?
The Plates Of A Parallel Plate Capacitor Are Charged By A Battery And The Battery Is Disconnected After The Charging. Now, The Plates Are Placed As Shown In The Figure. Then (Plates Are Not Parallel To Each Other)
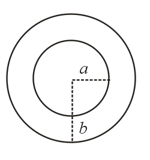
In the system of concentric thin conducting spherical shells of radii 'a' and 'b', the:
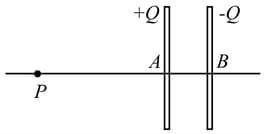
Two identical thin dielectric plates each of area carrying uniform charges and are placed parallel to each other. Both the plates have small holes and at their centres. Distance between the plates and size of holes are so small as compared to their linear dimensions that electric field between them can be assumed almost uniform and fringing of field near the edges can be ignored. A particle of mass and charge placed on the line joining the holes and at a great distance as shown in the figure. It is projected towards the capacitor with a velocity that is twice of the minimum velocity required to pass through the capacitor. The particle exits the capacitor with a speed . Calculate value of ?
A parallel plate air capacitor is connected to a battery. The quantities-charge, potential difference, electric field and stored energy associated with the capacitor are and respectively. A dielectric slab is now introduced with battery still connected. The dielectric constant of the dielectric is, . If final energy find .
A parallel plate capacitor of plate area and spacing is charged to volt and then disconnected from the battery, and pulled apart to double the plate spacing
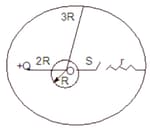
Two uncharged thin concentric spherical conducting shells '' and '' of radii and are connected through a resistance '' and switch '' initially opened as shown in the figure. A positive point charge '' is fixed at a distance from the centre of the shells. At , the switch ' ' is closed till the steady state is reached. Then choose the correct options(s)
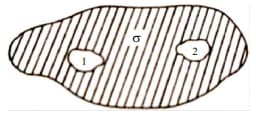
Two metal objects are embedded in infinitely large sample of weakly conducting material of conductivity and dielectric constant as shown in figure. A battery of voltage is connected between and . Now the battery is disconnected and the charge gradually leaks off through the material. The capacitance between the metal objects is and resistance between them is . Choose the correct statement(s):
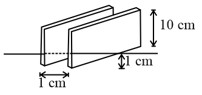
Consider the situation shown in the figure. The width of each plate is b. The capacitor plates are rigidly clamped in the laboratory and connected to a battery of emf . All surfaces are frictionless. The value of for which the dielectric slab will stay in equilibrium is
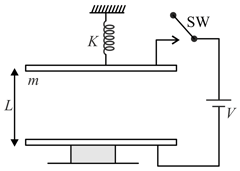
An uncharged parallel plate capacitor having its lower end fixed and upper end is attached with spring having spring constant . Upper plate is in equilibrium before switch is closed. After switch is closed, the condition on the potential of battery so that the system can acquire new equilibrium position without discharging is . Then is ? [ and are smallest possible positive integers and is potential difference across the battery. Ignore gravity]
A large vessel is filled with water having dielectric constant . Two square plates each of length and separated by are held parallel to each other with their lower ends just touching the surface of water. The plates are charged by applying a voltage and then disconnected from the voltage source. The liquid rises by between the plates. The capacitor has capacitances and without and with water respectively. Then