Electric Dipole
Electric Dipole: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Force on a Dipole in Uniform Electric Field, Torque on a Dipole in Electric Field, Oscillation of a Dipole in Electric Field & Time Period of an Oscillating Dipole in Electric Field etc.
Important Questions on Electric Dipole
Which orientation of an electric dipole(p) in a uniform electric field(E) would correspond to stable equilibrium?
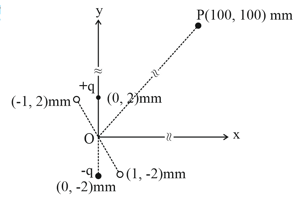
An electric dipole is formed by two charges and located in -plane at and , respectively, as shown in the figure. The electric potential at point due to the dipole is . The charges and are then moved to the points and , respectively. What is the value of electric potential at due to the new dipole?
A small dipole of dipole moment is placed at a distance from the centre of a neutral conducting sphere of radius The direction of dipole is towards the centre of the sphere. A tangent is drawn from the centre of dipole to the sphere which meets the sphere at point
An electric dipole moment It is placed in a uniform electric field
Two identical dipoles of dipole moment is a positive constant) are placed on axis at points and as shown. Then pick up the correct statements:
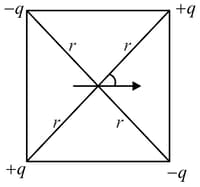
Given square frame of diagonal length $2 r$ made of insulating wires. There is a short ideal electric dipole, having dipole moment , fixed in the plane of the figure lying at the centre of the square, making an angle as shown in figure. four identical particles having charges of magnitude each and alternatively positive and negative are placed at the four corners of the square. Select the correct alternative(s). (neglect gravitationa effects) (Centre of dipole coincidence with the intersecting point of diagonals)
An electric dipole of moment p is placed in an electric field of intensity E. The dipole acquires a position such that the axis of the dipole makes an angle with the direction of the field. Assuming that the potential energy of the dipole to be zero when , the torque and the potential energy of the dipole will respectively be
A tiny electric dipole ( molecule) of dipole moment is placed at a distance form an infinitely long wire, with its normal to the wire in the same plane. If the linear charge density of the wire is the electrostatic force acting on the dipole is equal to . Obtain the value of
The dipole moment of a system of charge distributed uniformly on an arc of radius subtending an angle at its centre where another charge is placed is . Find the value of . Given
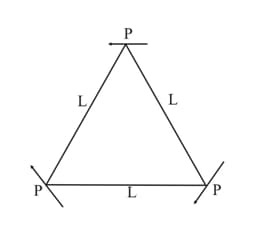
Three short electric dipoles, each of dipole moment are placed at the vertices of an equilateral triangle of side length Each dipole has its moment, oriented parallel to the opposite side of the triangle as shown in the fig. The electric field strength at the centroid of the triangle is Then value of is :
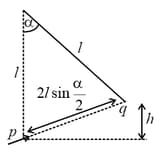
A point charge of mass is suspended vertically by a string of length A point dipole of dipole moment is now brought towards from infinity so that the charge moves away. The final equilibrium position of the system including the direction of the dipole, the angles and distances is shown in the figure below. If the work done in bringing the dipole to this position is where is the acceleration due to gravity, then the value of is (Note that for three coplanar forces keeping a point mass in equilibrium, is the same for all forces, where is any one of the forces and is the angle between the other two forces)
The electric potential at the equatorial position due to the dipole is zero.
Calculate the electric field due to a dipole at a point on the equatorial plane.
An electric dipole of length is placed with the axis making an angle of to an electric field of strength . If it experiences a torque of , the potential energy (in joule) of the dipole is . Find the value of .
If an electric dipole is placed in a uniform electric field, it experiences:
What is the unit of electric dipole moment?
Electric field due to the electric dipole at the equatorial plane is given as:
An electric dipole is formed by two equal and opposite charges with separation . The charges have same mass . It is kept in a uniform electric field . If it is slightly rotated from its equilibrium orientation, then its angular frequency to is :
An electric dipole is placed in a uniform electric field. Assuming the angle between the electric field and dipole axis is , the dipole will experience
