Electric Field
Electric Field: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Electric Field, Inverse Square Law, Electric and Gravitational Field, Electric Field Due to a Point Charge, Electric Field near a Conductor, Graph of Electric Field Due to Point Charge, Test Charge, etc.
Important Questions on Electric Field
A charge q is placed at the centre of the line joining two equal charges Q. The system of three charges will be in equilibrium if
Four charges are placed at the corners of a square taken in order. At the center of the square (Where -resultant electric field, - net potential)
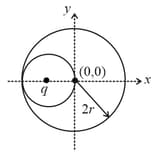
In a conducting metallic sphere of radius , an spherical cavity of radius is made. A charge is kept at the centre of the cavity as shown in the figure. Find the magnitude of the total electric field at
Assertion: Due to two point charges electric field and electric potential cannot be zero at some point simultaneously.
Reason: Field is a vector quantity and potential is a scalar quantity.
Two point charges and are placed some distance apart. If the electric field at the location of be , then that at the location of will be
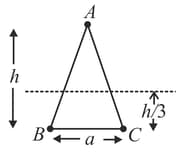
Two equal positive charges are placed at the vertices and of an isosceles triangle of base and height , as shown in the adjacent figure. When a charge is placed at it is found that at a point inside the triangle, the net electric field due to the three charges vanishes. If this point is at a height then what is ?
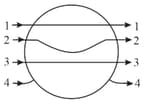
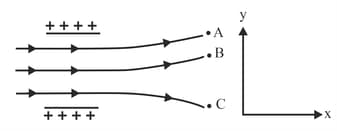
The tracks of three charged particles in a uniform electrostatic field are shown in the figure. Which particle has the highest charge to mass ratio?
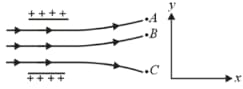
A metallic shpere is placed in a uniform electric field. The line of force follow the path(s) shown in the figure as,
The maximum field intensity on the axis of a uniformly charged ring of charge and radius will be
A thin conducting ring of radius is given a charge . The electric field at the centre of the ring due to the charge on the part of the ring is . The electric field at the centre due to the charge on the part of the ring is
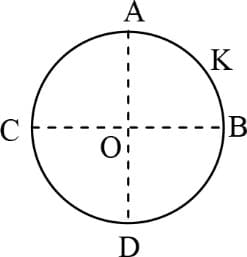
The tracks of three charged particles in a uniform electrostatic field are shown in the figure. Which particle has the highest charge to mass ratio?
Two point charges of and are apart where will the electric field strength be zero on the line joining the charges from charge
A small metal ball is suspended in an uniform electric field with the help of an insulated thread. If a high energy -ray beam falls on the ball, then the ball
The electric intensity outside a charged sphere of radius at a distance is
The minimum strength of a uniform electric field that can tear a conducting neutral thin-walled sphere into two equal parts is known to be . Then determine the minimum electric field strength required to tear a sphere of one-fourth of the radius with the same wall thickness.
Two mutually perpendicular infinitely long straight conductors carrying uniformly distributed charges of linear densities and are positioned at a distance from each other.
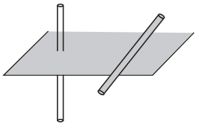
Force between the conductors depends on as
Two masses and carry positive charges and respectively. They are dropped to the floor in a laboratory set up from the same height, where there is a constant electric field vertically upwards. hits the floor before . Then,
Two masses and carry positive charges and , respectively. They are dropped to the floor in a laboratory set up from the same height, where there is a constant electric field vertically upwards. hits the floor before . Then,