Electric Potential and Potential Energy
Electric Potential and Potential Energy: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Electric Potential, Electric Potential in Terms of Electric Field, Potential Difference, Potential Difference in Uniform Electric Field, Potential Difference between Two Points in Uniform Electric Field, etc.
Important Questions on Electric Potential and Potential Energy
How does the electric potential due to a dipole vary on the dipole axis as a function of – distance of the field point from the mid–point of the dipole, at large distances?
Two point charges C and C are separated by a distance of 50 cm in air.
(i) Find the point on the line joining the charges, where the electric potential is zero.
(ii) Also find the electrostatic potential energy of the system.
Three charges, and , are placed at equal distances, on a straight line. If the potential energy of the system of three charges is zero, then what is the ratio of ?
Three charges, and , are placed at equal distances, on a straight line. If the potential energy of the system of three charges is zero, then what is the ratio of ?
The electric potential due to a system of charge in space is given by , where are the co-ordinates in metre and is in volts. The electric field intensity at along direction is
What is the electric potential inside a solid sphere?
Which of the follow graph is correct for potential due to point charge at any point versus distance as shown in figure.
The graph of variation of potential due to point charge vs distance is said to be _____ symmetric
A charge of is carried by the potential difference of then potential energy is
Electrostatic potential energy of single change in absence of external electric field is expressed as
A metallic sphere A isolated from the ground is charged to . This sphere is brought in contact with other isolated metallics sphere B of half the radius of sphere A. The charge on the two sphere will now be in the ratio
In the region where the electric field is zero, the relation between the electric potential and distance is,
A solid sphere of radius is charged uniformly. The distance from its surface at which the electrostatic potential is half the potential at the centre of the sphere is
The potential at a point due to some charge is given by equation volts. Then electric field at is given by
Which is the quantity that is equal to the work done on a unit positive charge to move it from infinity to a point in space?
The potential at a point due to a charge of located away is (Assume )
The maximum electric field that can be held in air without producing ionisation of air is . The maximum potential therefore, to which a conducting sphere of radius can be charged in air, is :
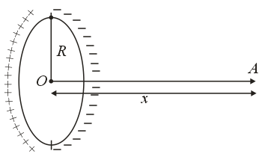
Half of the non-conducting ring has charge and half has charge. Find potential at point which is on the line passing through centre perpendicular to plane of ring.
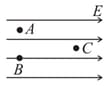
Suppose a region of space has a uniform electric field, directed towards the right, as shown below. Which statement is true ?
Electric field at a distance from the origin is given as Then potential difference between the points situated at and is :-
