Electric Potential and Potential Energy
Electric Potential and Potential Energy: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Electric Potential, Electric Potential due to a Point Charge at a Point, Electric Potential due to Two or More Charges at a Point, Electric Potential in Terms of Electric Field, etc.
Important Questions on Electric Potential and Potential Energy
A particle of charge+q and mass m moving under the influence of a uniform electric field E enters in I quadrant of a coordinate system at a point (0, a) with initial velocity vand leaves the quadrant at a point (2a, 0) with velocity .
Find Rate of work done by the electric field at point (0, a)
The term ‘potential energy’ of charge ‘q’ at a distance ‘r’ in an external electric field can be defined as:.
A charge is placed on a large spherical conducting shell of radius . Another small conducting sphere of radius r carrying charge is introduced inside the large shell and is placed at its centre. The potential difference between two points, one lying on the sphere and the other on the shell would be:
Two point charges C and C are separated by a distance of 50 cm in air.
(i) Find the point on the line joining the charges, where the electric potential is zero.
(ii) Also find the electrostatic potential energy of the system.
Two point charges are separated by a distance of 1m in air. Calculate at what point on the line joining the two charges is the electric potential zero.
Three charges, and , are placed at equal distances, on a straight line. If the potential energy of the system of three charges is zero, then what is the ratio of ?
Two point charges and are located at and respectively. Assume that the potential is vanishing at infinity. The correct statement about the surface (at finite distance) is:
The potential for a point charge placed at a distance from a grounded infinite conducting plate is
Here is a constant. The maximum value of induced charge density on the conducting plate is
A charge is distributed over a thin ring of radius with line charge density . Note that the ring is in the plane and is the angle made by with the -axis. The work done by the electric force in displacing a point charge from the center of the ring to infinity is
4. .
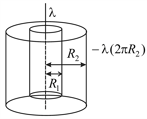
A long wire with a uniform linear charge density is placed along the common axis of two long coaxial thin cylindrical shells of radii and (see figure). The outer shell carries a uniform surface charge density . Take the zero of the potential at infinity along the radial direction. The potential at a distance $r$ from the axis where is
Three charges, and , are placed at equal distances, on a straight line. If the potential energy of the system of three charges is zero, then what is the ratio of ?
The electric field due to an extended charge distribution spread over all space is given by
Here and are positive constants and the electrostatic potential is taken to be zero at infinity. Select the correct statement(s).
Which of the following statements are correct? If the potential along the straight line joining the two charges and , separated by a distance , is represented as shown in the figure below.
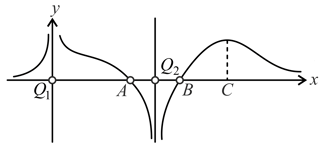
- is positive in nature
- are equilibrium points
- is a point of unstable equilibrium along axis.
If the potential difference between the surface of hollow charged metal sphere of radius and a point at a distance from the centre is , then the electric intensity at a distance from the centre is-
Two positive charges and are apart. The work done in bringing them closer to is
An uncharged conductor $A$ is brought near a positively charged conductor $B$, then :
When a charge is carried from point to point , the amount of work done by the electric field is . What is the potential difference and which is at a higher potential?
Electric potential due to point charge in air is expressed as as . i.e for to potential varies
The graph of variation of potential due to point charge vs distance is said to be symmetric
The electrostatic energy of a nucleus of charge is equal to , where is a constant and is the nuclear radius. The nucleus divides into two daughter nuclei of charges and equal radii. The change in electrostatic energy in the process when they are far apart is
