Gauss's Law
Gauss's Law: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Electric Flux, Area Vector, Proof of Coulomb's Law Using Gauss Law & Proof of Gauss Law etc.
Important Questions on Gauss's Law
The electric field components due to a charge inside the cube of side are as shown:
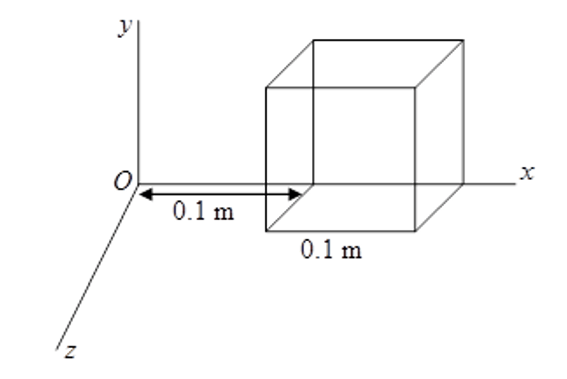
, where
.
Calculate the flux through the cube, and the charge inside the cube.
Which law is used to derive the expression for the electric field between two uniformly charged large parallel sheets with surface charge densities and respectively:
Applying Gauss theorem, the expression for the electric field intensity at a point due to an infinitely long, thin, uniformly charged straight wire is
A hollow charged metal sphere has radius . If the potential difference between its surface and a point at a distance from the centre is, then electric field intensity at a distance is:
An electric field is present to a square plate of side length . What is the flux passing through the plate?
A charge is distributed uniformly in a sphere (solid). Then the electric field at any point , where ( is radius of sphere) varies as_____.
Two infinitely long parallel conducting plates having surface charge densities and respectively are separated by a small distance. The medium between the plates is vacuum, if is dielectric permittivity of vacuum, then the electric field in the region between the plates is-
A cylinder of radius and length is placed in a uniform electric field parallel to the cylinder axis. The total flux for the surface of the cylinder is given by
E signifies the _____ passing through a certain area dS. is the total amount of charge and signifies the permittivity of the vacuum.
Assertion: Gauss's law can't be used to calculate electric field near an electric dipole.
Reason: Electric dipole don't have symmetrical charge distribution.
Area vector is a vector quantity associated with each plane figure whose magnitude is
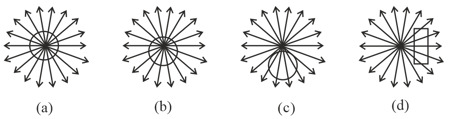
The black shapes in the figure below are closed surfaces. The electric field lines are in red. For which case, the net flux through the surfaces is non-zero?
Let the electrostatic field, at distance, from a point charge, not be an inverse square but instead an inverse cubic, e.g. , here is a constant. Consider the following two statements: (I) Flux through a spherical surface enclosing the charge is, . (II) A charge placed inside a uniformly charged shell will experience a force. Which of the above statements are valid?
A point electric charge is placed at a corner of a cube as shown in the figure. What is the electric flux passing through of the cube? ( is permittivity of free space)
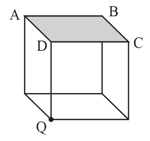
A point charge is placed at the center of a cube of side in vacuum (permitivity The flux of the electric field through the shaded face is given by
A sphere of radius carries a positive charge density that increases linearly with radial distance from the centre The radial dependence of the magnitude of electric field inside the sphere is given by
A hollow cylinder has a charge coulomb within it. If is the electric flux in units of associated with the curved surface , the flux linked with the plane surface in units of will be