Gauss’s Law
Gauss’s Law: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Area Vector, Electric Flux, Electric Flux from a Surface Due to Point Charges, Electric Flux from a Surface in Electric Field, and Electric Flux through a Closed Surface in Uniform Electric Field.
Important Questions on Gauss’s Law
The electric field components due to a charge inside the cube of side are as shown:
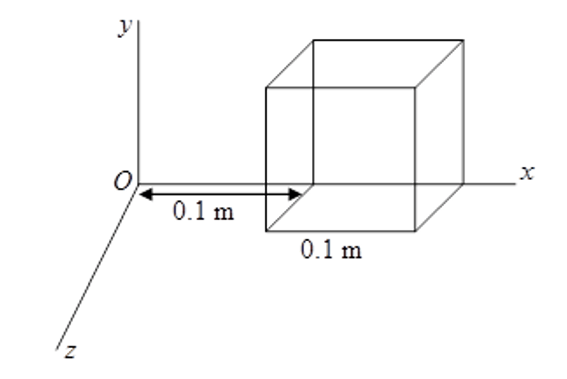
, where
.
Calculate the flux through the cube, and the charge inside the cube.
Which law is used to derive the expression for the electric field between two uniformly charged large parallel sheets with surface charge densities and respectively:
Applying Gauss theorem, the expression for the electric field intensity at a point due to an infinitely long, thin, uniformly charged straight wire is
A hollow charged metal sphere has radius . If the potential difference between its surface and a point at a distance from the centre is, then electric field intensity at a distance is:
A cylinder of radius and length is placed in a uniform electric field parallel to the cylinder axis. The total flux for the surface of the cylinder is given by
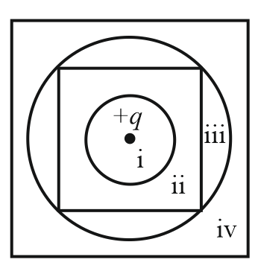
Figure shows, in cross section, two Gaussian spheres and two Gaussian cubes that are centered on a positively charged particle. Select the correct alternatives.
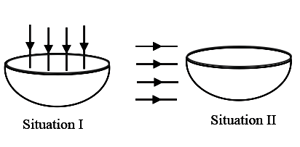
In the figure, a hemispherical bowl of radius is shown. Electric field of intensity is represented in each situation by direction lines.
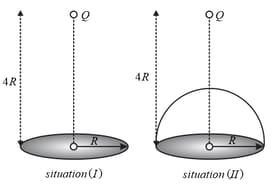
A positive point charge is placed (on the axis of the disc) at a distance of above the center of a disc of radius as shown in situation The magnitude of electric flux through the disc is Now, a hemispherical shell of a radius is placed over the disc such that it forms a closed surface as shown in situation The flux through the curved surface in the situation taking direction of area vector along outward normal as positive is
In the figure shown, there is a large sheet of charge of uniform surface charge density . A charge particle of charge and mass is projected from a point on the sheet with a speed with angle of projection such that it lands at maximum distance from on the sheet. Neglecting gravity, find the time of flight.
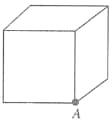
The total flux through the faces of the cube with side of length if a charge is placed at corner of the cube is
A point charge of is at the centre of cubical Gaussian surface on edge. What is the net electric flux through the surface?
A ring of radius having a linear charge density moves towards a solid imaginary sphere of radius so that the centre of ring passes through the centre of the sphere. The axis of the ring is perpendicular to the line joining the centres of the ring and the sphere. The maximum flux through the sphere in this process is
A conducting spherical shell of radius has a charge units. The electric field due to the shell at a point
Flux coming out from a unit positive charge enclosed in air is
A Gaussian sphere encloses an electric dipole within it. The total flux across the sphere is
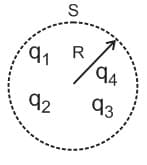
and are point charges located at points, as shown in the figure, and is a spherical Gaussian surface of radius . Which of the following is true, according to the Gauss' law?
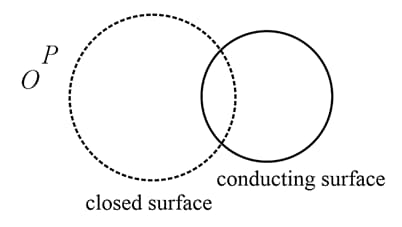
The figure shows a closed surface which intersects a conducting sphere. If a positive charge is placed at the point , the flux of the electric field through the closed surface,
In a region of space having a spherically symmetric distribution of charge, the electric flux enclosed by a concentric spherical Gaussian surface varies with a radius as
where and are the constants.
The electric field strength in the region is given as,
A Gaussian sphere encloses an electric dipole within it. The total flux through the sphere is
