Principle of Superposition
Principle of Superposition: Overview
This topic covers the concept of superposition principle.
Important Questions on Principle of Superposition
A hemisphere is uniformly charged positively. The electric field at a point on a diameter away from the centre is directed
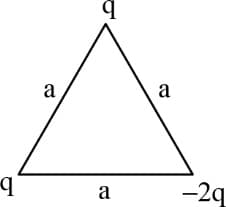
Three charges each of are placed at the corners of an equilateral triangle. If the force between any two charges be , then the net force on either charge will be:
Three large identical conducting sheets, each having a surface area of is placed parallel to each other at finite distance contain charges and . What is the magnitude of electric field at point?
Which of the following figures correctly shows the top view sketch of the electric field lines for a uniformly charged hollow cylinder as shown in figure? 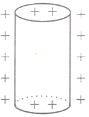
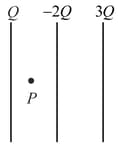
A charge is located at the origin in free space and another charge at . If the -component of the electric field at is zero, then the magnitudes of in is
A uniform surface charge density exists over the entire plane except for a circular hole of radius a centred at the origin. The electric field at a point on the -axis is found to be
In a regular polygon of sides, each corner is at a distance from centre. Identical charges of magnitude are placed at corners. The field at the centre is
A regular polygon has sides. Equal charges, each , are placed at vertices of the polygon and a charge is placed at the centre of the polygon. If the distance of each vertex from the centre is , net force experienced by is
In the basic crystal structure, and ions are arranged in a BCC configuration as shown in Fig. The net electrostatic force exerted by the eight ions on the ion is
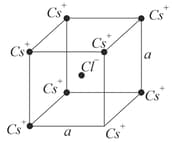
Four equal charges, each are placed at the four corners of a square of side . Then the Coulomb force experienced by one charge due to the rest of three is
If two like charges of magnitude and are separated by a distance of , then the point on the line joining the charges, where the force experienced by a charge placed at that point is zero, is
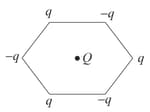
Vertices of a regular hexagon, of sides , have three positive and three negative charges, each of magnitude , as shown in the diagram. A point charge of is placed at the centre of the hexagon. The net force on is
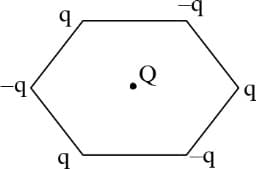
Vertices of a regular hexagon of sides have three positive and negative charges each of magnitude as shown in diagram. A point charge of is placed at centre of hexagon. The net force on is -
Three charges are placed at the vertices of an equilateral triangle of sides . The force experienced by the charge placed at the vertex in a direction normal to is
The charge is placed at each of the two opposite corners of a square and a charge is placed at each of the other two opposite corners. If charges are fixed, then for equilibrium of , it is required that-
Two identical balls each having a density are suspended from a common point by two insulating strings of equal length. Both the balls have equal mass and charge. In equilibrium, each string makes an angle with the vertical. Now, both the balls are immersed in a liquid of density , but the angle does not change. The dielectric constant of the liquid is -
If two like charges of magnitude coulomb and coulomb are separated by a distance of , then the point on the line joining the charges, where the force experienced by a charge placed at that point is zero, is
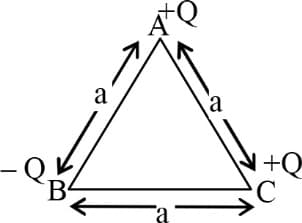
Charges and are placed at the corners , and of an equilateral triangle . If is the electric field at the circumcentre of the triangle, due to the charge , then the magnitude and direction of the resultant electric field at is:
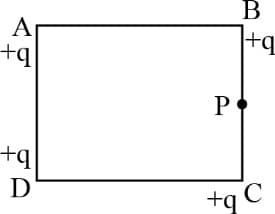
Four charges, each having charge , are located at the vertices of square of side as shown in the figure. Find the electric field at the mid-point of side .