Calculation of Electric Potential
Calculation of Electric Potential: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Electric Potential due to a Charged Ring on Its Axis and Electric Potential on the Axis of Charged Disc.
Important Questions on Calculation of Electric Potential
What is the potential electric energy of a charged object?
What is the electric potential due to an electric?
What is the electric potential of a point charge?
What is the electric field on the axis of a charged ring?
How much work is done in moving a charge of across two points having a potential difference of ?
A rod lies along the axis with one end at the origin and other at it caries a uniform charge . Find the electric field at the point on the axis
A total charge is distributed uniformly along a straight rod of length . The potential at a point at a distance from the midpoint of the rod is
Consider a non-conducting rod of length having a uniform change density . Find the electric potential at at a perpendicular distance above the midpoint of the rod.
The electric potential due to an infinite uniformly charge of linear charge density at a distance from it is given by is the reference point.
A charge is distributed over a thin ring of radius with line charge density . Note that the ring is in the -plane and is the angle made by with the -axis. The work done by the electric force in displacing a point charge from the centre of the ring to infinity is
Two identical rings each of radius are coaxially placed distance apart. They carry charges and respectively. If a charge is moved from the centre of one ring to the centre of the other ring, the work done is
Half of the non-conducting ring has charge and half has charge. Find potential at point which is on the line passing through centre perpendicular to plane of ring.
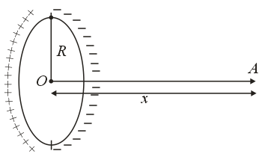
A thin ring of radius has been uniformly charged with an amount of and placed in relation to a conducting sphere in such a way that the centre of the sphere , lies on the rings axis at a distance of from the plane of the ring. The potential of the sphere is ………. volt.
(Given: )
A thin ring of radius has been uniformly charged with an amount of and placed in relation to a conducting sphere in such a way that the centre of the sphere , lies on the rings axis at a distance of from the plane of the ring. The potential of the sphere is………. volt.
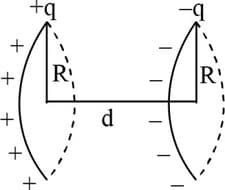
Two thin rings, each of radius , are placed at a distance apart. The charges on the rings are and , respectively. The potential difference between their centres will be
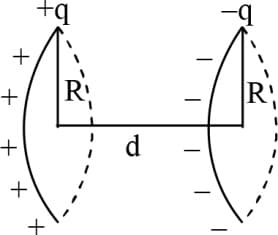
Two thin rings each of radius are placed at a distance apart. The charges on the rings are and . The potential difference between their centres will be -
A non-conducting ring of radius carries total charge of distributed non-uniformly on its circumference producing an electric field everywhere in space.
The value of the line integral ( being centre of the ring) in volt is
A non-conducting ring of radius carries a total charge of distributed non-uniformly on its circumference producing an electric field , everywhere in space. The value of the line integral, in S.I. System of units following usual convention, where, is the centre of the ring is:
A non-conducting disc, of radius and uniform positive surface charge density is placed on the ground with its axis vertical. A particle of mass and positive charge is dropped, along the axis of the disc from a height with zero initial velocity. The particle has . What is the stable equilibrium position of the particle?
A non-conducting disc, of radius and uniform positive surface charge density is placed on the ground with its axis vertical. A particle of mass and positive charge is dropped, along the axis of the disc from a height with zero initial velocity. The particle has, . What is the value of if the particle just reaches the disc?