Biot-Savart Law
Biot-Savart Law: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Biot-Savart Law, Permeability of Free Space, Permeability of a Medium, Current Element, Magnetic Field Due to a Current, Magnetic Field of a Moving Charge & Relative Permeability of a Medium etc.
Important Questions on Biot-Savart Law
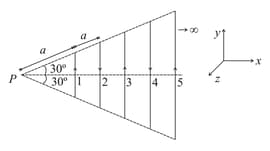
Infinite number of straight wires each carrying current I are equally placed as shown in the figure. Adjacent wires have current in opposite direction. Net magnetic field at point P is.
Three infinitely long thin wires each carrying current in the same direction, are in the x-y plane a gravity-free space. The central wire is along the y-axis while the other two are along Find the locus of the points for which the magnetic field B is zero.
Find the magnetic induction at point , if the current carrying wire is in the shape shown in the figure.
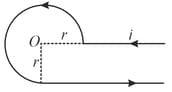
Find the magnetic induction at the origin in the figure shown.
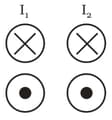
A system of long four parallel conductors whose sections with the plane of the drawing lie at the vertices of a square there flow four equal currents. The directions of these currents are as follows : those marked point away from the reader, while those marked with a dot point towards the reader. How is the vector of magnetic induction directed at the centre of the square ?
A long straight wire carries a current of directed along the negative axis as shown in the figure. A uniform magnetic field of magnitude is directed parallel to the axis. What is the resultant magnetic field at the following point ?
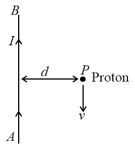
A long straight wire carries a current . A proton travels with a speed , parallel to the wire, at a distance from it in a direction opposite to the current as shown in the figure. What is the force experienced by the proton and what is its direction?
Define the relative permittivity of a medium.
The relative permeability of a medium is . What is the magnetic susceptibility.
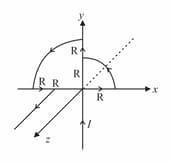
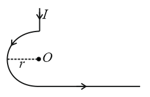
A current carrying circular arc wire of the length is turned along a circle, as shown in the figure. The magnetic field at the centre .
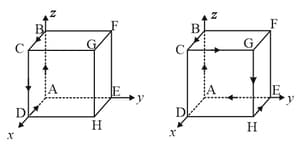
The current in flowing along the path of a cube (shown in the left figure) produces a magnetic field at the centre of cube of magnitude . Dashed line depicts the non-conducting part of the cube.
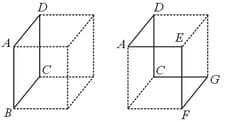
Consider a cubical shape shown to the right which is identical in size and shape to the left. If the same current now flows in along the path , then the magnitude of magnetic field at the centre will be
An electron moving in a circular orbit of radius makes revolution per second. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field strength at the centre ?
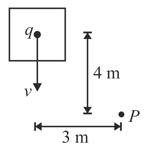
An elevator carrying a charge of is moving down with a velocity of . The elevator is from the bottom and horizontally from as shown in the figure. What magnetic field in does it produce at point .
A square loop of side carries a current . Calculate magnetic induction at point , lying on the axis of loop and at a distance from the center of loop.
A long straight wire in the horizontal plane carries a current of 75 A in north to south direction, magnitude and direction of field B at a point 3 m east of the wire is
A magnetic intensity of produces a flux of in a iron bar of cross sectional area . The permeability of the iron bar is
If magnetic field at point is Tesla. Determine current ?
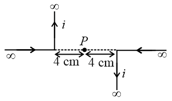
In the given figure, what is the magnetic field induction at point .
Current is flowing along the path ABCD, along the four edges of the cube (figure-a), creates a magnetic field in the centre of the cube of . Find the magnetic field B created at the centre of the cube by a current flowing along the path of the six edges ABCGHEA (figure-b)
A square loop is made by a uniform conductor wire as shown in figure
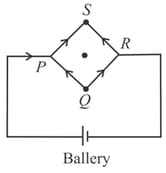
The net magnetic field at the centre of the loop if side length of the square is a
