Force Between Two Parallel Current - Carrying Conductors
Force Between Two Parallel Current - Carrying Conductors: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Force between Two Parallel Current Wires & One Ampere Electric Current etc.
Important Questions on Force Between Two Parallel Current - Carrying Conductors
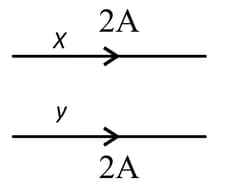
In given figure, X and Y are two long straight parallel conductors each carrying a current of 2 A. The force on each conductor is F newtons. When the current in each is changed to 1 A and reversed in direction, the force on each is now
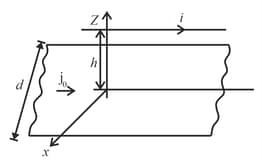
A conductor wire carrying current is placed symmetrically and parallel to a long conducting sheet having a current per unit width and width , as shown in the figure. the force per unit length on the conductor wire will be
Which of the following expressions correctly describes for the force between two long parallel current carrying conductors:
What is the expression for the force acting per unit length on one conductor due to the other for two parallel wires.
The force acting per unit length on one conductor due to the other for two long parallel current-carrying wires is
Two straight parallel wires, both carrying amperes currents in the same direction attracts each other with a force of . If both currents are doubled, the force of attraction will
Two infinite line-charges parallel to each other are moving with a constant velocity in the same direction as shown in the figure. The separation between two line-charges is . The magnetic attraction balances the electric repulsion when, [speed of light in free space]
The force between two parallel current carrying conductors separated by a distance is . If the current in each conductor is doubled and the distance between them is halved, then the force between them becomes-
A current of passes through two very long wires held parallel to each-other and separated by a distance of . The force per unit length between them is . Find the value of .
A current of passes through two very long wires held parallel to each-other and separated by a distance of . The force per unit length between them is . Find the value of .
A current of passes through two very long wires held parallel to each other and separated by a distance of The magnitude of force per unit length between them is [Use in S.I. unit]
Through two parallel wires and and ampere of currents are passed respectively in opposite direction. If the wire A is infinitely long and the length of the wire is the force on the conductor which is situated at distance from will be :-
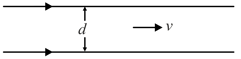
Two wire of length each are parallel and are at a distance from each other. If the current in both the wires is in the same direction. Find force per unit length on them.
Two horizontal parallel straight conductors, each long, are arranged one vertically above the other, and carry equal currents in opposite directions. The lower conductor is fixed while the other is free to move in guides remaining parallel to the lower. If the upper conductor weighs , what is the approximate current (in ) that will remain the conductors at a distance apart?
A rectangular conducting loop carrying a current is situated near a long straight wire carrying a steady current . The wire is parallel to one of the sides of the loop and is placed in the same plane as that of the loop as shown in the figure. Then, the current loop will
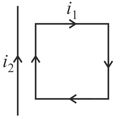
Figure shows a square loop of length on each side in the plane with its centre at the origin. The loop carries a current of . Above it at is an infinitely long wire parallel to the axis carrying a current of . The net force on the loop is . Write the value of to the nearest integer.
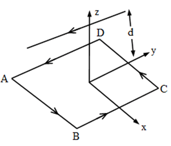
A long straight wire carrying current of rests on a table. Another wire of length , mass carries the same current but in the opposite direction, the wire is free to slide up and down. The height upto which will rise is
Two straight wires and of lengths and carrying currents of and respectively in opposite directions, lie parallel to each other at a distance of . The force on a section of the wire near its centre is
A conductor of length carrying current is held parallel to an infinitely long conductor carrying current of at a distance of , the force on small conductor is
Two very long straight parallel wires carry steady currents and , respectively. The distance between the wires is . At a certain instant of time, a point charge is at a point equidistant from the two wires in the plane of the wires. Its instantaneous velocity is perpendicular to this plane. The magnitude of the force due to the magnetic field acting on the charge at this instant is
