Tangent Law
Tangent Law: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Tangent Law, Tangent Galvanometer, Principle of Tangent Galvanometer & Theory of Working of Tangent Galvanometer etc.
Important Questions on Tangent Law
What is the main purpose of the tangent galvanometer experiment?
A tangent galvanometer of reduction factor is placed with plane of its coil perpendicular to the magnetic meridian when a current of is passed through it. The defection produced is
The sensitivity of a tangent galvanometer increases, if
The tangent galvanometer, when connected in series with a standard resistance can be used as
Two tangent galvanometers having coils of the same radius are connected in series. A current flowing in them produces deflections of and respectively. The ratio of the number of turns in the coils is
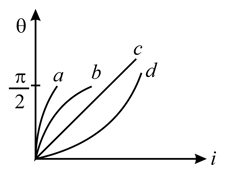
The curve that may best represent the current vs deflection in a tangent galvanometer is
Consider two short magnets and whose lengths are in ratio and the pole strength are in ratio. The magnet produces a deflection when placed at a certain distance in position of the magnetometer. If the magnet is placed at the same distance in position of the magnetometer, then find the deflection produced:
A coil carrying a heavy current and having large number of turns is mounted in a N - S vertical plane. A current flows in the clockwise direction. A small magnetic needle at its centre will have its north pole is
A rectangular coil cm consisting of 100 turns caries 0.1 A. If it produces a deflection , in a field of induction 0.1T, the couple per unit twist is
Assertion: A tangent galvanometer is used for measuring current.
Reason: As it is direct reading.
Assertion: Reduction factor of a tangent galvanometer helps in reducing the deflection of a current.
Reason: Reduction factor increases with increase in current.
The tangent galvanometers having coils of the same radius are connected in series. A current flowing in them produces deflections of and respectively. The ratio of the number of turns in the coil is -
A short magnet produces a deflection of when placed at certain distance in position of magnetometer. If another short magnet of double the length and thrice the pole strength is placed at the same distance in position of the magnetometer, the deflection produced will be
A tangent Galvanometer is connected directly to an ideal battery. If the number of turns in the coil is doubled, the deflection will
Two tangent galvanometers and have coils of radii and respectively and resistance each. They are connected in parallel with a cell of emf and negligible internal resistance. The deflections produced in the tangent galvanometers and are respectively. If has two turns, then must have
Two tangent galvanometers and have coils of radii and , respectively, and resistance each. They are connected in parallel with a cell of emf and negligible internal resistance. The deflections produced in the tangent galvanometers and are and , respectively. If has turns, then must have
A deflection magnetometer is placed with its arm along the east-west direction and a short bar magnet is placed symmetrically along its axis at some distance with its north pole pointing towards east. In this position the needle of the magnetometer shows a deflection of . If we double the distance of the bar magnet, then the deflection will be
A compass needle free to turn in a horizontal plane is placed at the centre of a circular coil of turns and radius . The coil is in a vertical plane making an angle of with the magnetic meridian. When the current in the coil is , the needle points west to east.
The current in the coil is reversed and the coil is rotated about its vertical axis by an angle of in the anticlockwise sense looking from above. Predict the direction of the needle. Take the magnetic declination at the places to be zero.
A compass needle free to turn in a horizontal plane is placed at the centre of circular coil of turns and radius . The coil is in a vertical plane making an angle of with the magnetic meridian. When the current in the coil is , the needle points west to east.
The current in the coil is reversed and the coil is rotated about its vertical axis by an angle of in the anticlockwise sense looking from above. Predict the direction of the needle. Take the magnetic declination at the places to be zero.
