Coulomb's Law for Magnetism
Coulomb's Law for Magnetism: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Permeability of Free Space, Permeability of a Medium, Relation between Permittivity and Permeability of Free Space, Magnetic Monopole, Relative Permeability of a Medium, Force between Two Monopoles, etc.
Important Questions on Coulomb's Law for Magnetism
On what factor does the pole strength of a magnet depends?
What happens pole strength?
Why unit of pole strength is ampere meter?
What is Coulomb's law in magnetism?
What is unit Pole?
Magnetic poles exist in _____.
How is the speed of light related to the permittivity and permeability of free space?
Which of the following equations correctly represents the relationship between permeability and permittivity of free space?
What is the relation between permeability and permittivity of free space?
Why we get two null points for a bar magnet? Can we get only one null point? How?
It's two magnetic poles of unit pole strength are at distance in vacuum. The force between them will be-
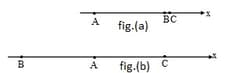
In figure three positively charged particles are fixed on an -axis. Particles and are so close to each other that they can be considered to be at the same distance from particle . The net force on particle due to particle and is in the negative direction of the -axis. In figure particle has been moved to the opposite side of but is still at the same distance from it. The net force on is now in the negative direction of -axis. The ratio of charge of particle to that of particle is : , then value of is
The refractive index and permeability of a medium are and respectively. The relative permittivity of the medium is nearly
A magnetic intensity of produces a flux of in a iron bar of cross sectional area . The permeability of the iron bar is
Assertion: Poles of a magnet can never be separated.
Reason: Since each atom of a magnetic material is a magnet in itself.
The characteristic impedance of free space is
Two disimilar poles of strength and are separated by a distance . If the null point is at a distance of from , then calculate
Six similar magnetic poles are placed on six corners of a regular haxagon of side . A south pole of strength is placed at the centre of hexagon. Find the magnetic force on the south pole
Three similar magnetic south poles each of strength are placed at the corners of an equilateral triangle of side . Find the magnetic force on one of the pole
Two similar equal poles magnet when separated by a distance of , they repel with a force of . The pole strength is
