Conduction
Conduction: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as The Steady State Heat Flow, Heat Flow and Area of Cross Section, Coefficient of Thermal Conductivity, Heat Flow through Slabs in Series, Heat Flow through Slabs in Parallel, Wiedemann-Franz law, etc.
Important Questions on Conduction
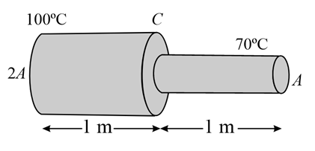
A metal rod of length has cross sectional areas and as shown in the figure. The ends are maintained at temperatures and . The temperature at middle point is___.
Which of these quantities does Weidemann-Franz law connect?
(i) Thermal conductivity
(ii) Electrical conductivity
(iii) Specific heat
For thermal conductivity , electrical conductivity , temperature and Lorenz number , which one of the following is the correct equation for Weidemann-Franz law?
For a long hollow cylinder maintained at uniform but different temperatures from its inner core to the outer surface, transfer of heat may be assumed to be taking place in which direction?
Which one of the following is correct for steady-state heat transfer in a conductor?
Here, is the heat energy transferred
And is time
One end of a uniform conductor of length and cross-sectional area is placed at freezing point and the other end is placed at the boiling point of water. If the material of this conductor has a thermal conductivity of , calculate the rate of heat energy transfer from the hot end to the cold end in the unit of .
Explain why does the temperature of a pan placed on a stove becomes constant after heating it for a while.
Wiedemann-Franz law shows that with the increase in velocity of particles inside a conductor, its thermal conductivity decreases and electrical conductivity increases.
During steady state, the flow of heat depends only on _______ of the conductor.
Thermometric conductivity describes how fast heat can transfer from a hot body to a cold body whereas thermal conductivity describes how well a material can spread heat.
Which one of the following is the correct SI unit for thermometric conductivity?
One end of a copper rod of length and area of cross-section is immersed in boiling water and the other end in ice. If the coefficient of thermal conductivity of copper is cal and the latent heat of ice is then the amount of ice which will melt (in grams) in one minute is
A copper rod of length and an iron rod of length having the same areas of cross section are connected in series. Thermal conductivities of copper and iron are respectively and units. The equivalent conductivity of the composite bar in unit is ____.
Heat is passed through two cylindrical rods of same material. Their diameters and lengths are in the ratio and respectively. If their ends are maintained at same temperature difference, the ratio of rate of flow of heat through them is
A long rod has one end at and other end at a high temperature. The coefficient of thermal conductivity varies with distance from the low temperature end as, , where SI unit and . At what distance from the first end, the temperature will be ? The area of cross-section is and rate of heat conduction is .
What is the rate of flow of heat through a tapering rod of length tapering from radius and when the temperature of the ends are and and coefficient of thermal conductivity is
An icebox almost completely filled with ice at is dipped into a large volume of water at . The box has walls of surface area , thickness and thermal conductivity . Calculate the rate at which the ice melts in the box. Latent heat of fusion of ice .
Water is boiled in a container having a bottom of surface area , thickness and thermal conductivity . of water is converted into steam in the steady-state after the boiling starts. Assuming that no heat is lost to the atmosphere, calculate the temperature of the lower surface of the bottom. Latent heat of vaporization of water .
The normal body-temperature of a person is . Calculate the rate at which heat is flowing out of his body through the clothes assuming the following values. Room temperature , surface of the body under clothes , conductivity of the cloth, thickness of the cloth
A liquid-nitrogen container is made of a thick styrofoam sheet having thermal conductivity . Liquid nitrogen at is kept in it. A total area of is in contact with the liquid nitrogen. The atmospheric temperature is . Calculate the rate of heat flow from the atmosphere to the liquid nitrogen.
