Newton’s Law of Cooling
Newton’s Law of Cooling: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Newton's Law of Cooling, Newton's Law of Cooling by Average Method, Newton's Law of Cooling by Calculus Method, Curve of Cooling of Hot Water with Time & Verification of Newton's Law of Cooling etc.
Important Questions on Newton’s Law of Cooling
An object cools from to in minutes, when the surrounding temperature is . Then the time taken by the object to cool from to is
[Take ]
A hot container takes min to cool from to . The time it takes to cool from to is
[consider the room temperature as ]
A brass boiler has a base area and thickness It boils water at the rate of when placed on a gas stove. Estimate the temperature of the part of the flame in contact with the boiler. Thermal conductivity of brass:
A body cools down from to in 10 minutes when the temperature of surrounding is . The temperature of the body after next 10 minutes will be:
A body cools from to If this takes time when the surrounding temperature is what will be the time taken if the surrounding temperature is
Two identical beakers and contain equal volumes of two different liquids at each and left to cool down. Liquid in has density of and specific heat of while the liquid in has density and specific heat of . Which of the following best describes their temperature versus time graph schematically? (assume the emissivity of both the beakers to be the same)
If a piece of metal is heated to temperature and then allowed to cool in a room which is at temperature, the graph between the temperature of the metal and time will be closest to :
Hot water in a vessel kept in a room, cools from to in minutes, from to in minutes and from to in minutes. Then,
The circuit below is used to heat water kept in a bucket.
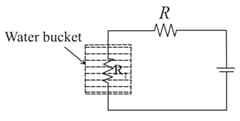
Assuming heat loss only by Newton's law of cooling, the variation in the temperature of the water in the bucket as a function of time is depicted by
A body cools down from to in time , from to in time and to in time . The correct statement according to Newtons law of cooling is
A cup of tea cools from to in one minute. The ambient temperature is In cooling from to it will take:
A calorimeter of water equivalent , takes to cool from to having of water. It takes to cool from to , if it is filled with of turpentine oil. Find the specific heat of turpentine oil.
The time required by two liquids to cool from to is and , respectively. What is the ratio of densities of these liquids if the ratio of specific heat of both are ? (water equivalent of the calorimeter is negligible)
It is known for a certain liquid that it takes to cool from to and to cool from to . Figure out the ambient temperature of the room.
Calculate the net rate of radiation loss from a solid cube of side , which has a temperature of while the ambient temperature is . It is given that the cube has an emissivity of .
"The rate of loss of heat of the body is directly proportional to the temperature difference of the body and surroundings". Choose the correct option related to this statement.
Steel is heated to temperature and then allowed to cool in a room which is at temperature, the graph between the temperature of steel and time will be closest to
A body cools in a surrounding of constant temperature . Its heat capacity is . The initial temperature of the body is . Assume Newton's law of cooling is valid. The body cools to in . In further it will cool from to
A body cools in from to What time (in min) does it take to cool from to if surrounding temperature is (Assume Newton's law of cooling)
A cup of tea cools from to in in a room at . How long will it take to cool from to in the same room?
