Assumptions of Kinetic Theory of Gases
Assumptions of Kinetic Theory of Gases: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Ideal Gas Assumptions,Large Number of Gas Molecules,Random Motion of Gas Molecules etc.
Important Questions on Assumptions of Kinetic Theory of Gases
If volume occupied by molecules is negligible, then what will be the pressure exerted by one mole of at is .
State the assumption regarding the volume of gas molecules to consider the gas as an ideal gas.
For gas to be ideal gas, it is assumed that the _____ of the molecules is negligibly small compared to the volume occupied by the gas.
A particle of mass and initial velocity collide with another particle of mass which is at rest, The collision is head on and perfectly elastic. The ratio of de Broglie wavelengths and after the collision is
A gas diffuse times as fast as hydrogen. Its molecular weight is
The average intermolecular distance is considerably small as compared to the diameter of the molecule.
State the basic assumptions of kinetic theory of gases.
What is an ideal gas or perfect gas? State equation of an ideal gas.
A sample of an ideal gas occupies a volume at pressure and absolute temperature . The mass of each molecule is , then the density of the gas is
When the temperature of a gas filled in a closed vessel is increased by , its pressure increases by percent. The initial temperature of gas was
A vessel has of oxygen at pressure and temperature . A small hole is made in it so that oxygen leaks out. How much oxygen leaks out if the final pressure is and temperature is ?
Two different isotherms representing the relationship between pressure and volume at a given temperature of the same ideal gas are shown for masses and of the gas respectively in the figure given, then
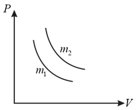
A graph between pressure (along -axis) and absolute temperature, (along -axis) for equal moles of two gases has been drawn. Given that volume of second gas is more than volume of first gas. Which of the following statements is correct?
The perfect gas equation for 4 g of hydrogen gas is
Two containers A & B contain ideal gases helium and oxygen respectively. Volume of both containers are equal and pressure is also equal. Container A has twice the number of molecules than container B then if & represent the rms speed of gases in containers A & B respectively, then -
Assertion: According to kinetic theory of gases, all the collision between molecule-molecule, and between molecule-walls of container are perfectly elastic, so speed of each molecule in an isolated gaseous system remains constant.
Reason: Distribution of speed among the molecules of gas does not change with time for the above system.
Assertion: The potential energy of ideal gas is zero.
Reason: At low pressure or high temperature the molecules are far apart and molecular interactions are negligible.
P-V diagram of a diatomic gas is a straight line passing through origin. The molar heat capacity of the gas in the process will be -
What is an ideal gas?
What is the average velocities of particles in a gas
