Law of Equipartition of Energy
Law of Equipartition of Energy: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Energy in Gases, Molar Kinetic Energy, Molecular Kinetic Energy, Degrees of Freedom of Gas Molecule, Translational Degree of Freedom, Rotational Degree of Freedom, and Vibrational Degree of Freedom.
Important Questions on Law of Equipartition of Energy
Rigid diatomic molecules of gas have how many rotational degrees of freedom?
The total number of degrees of freedom for a non-rigid diatomic molecule is equal to:
The number of translational degrees of freedom for a diatomic gas is
Two ideal monatomic gases and at and are mixed. The number of moles in gas is and number of moles in gas is . What will be the temperature of the mixture?
According to the kinetic theory of gases, for a diatomic molecule
Molecule of a gas can be modelled as three sphere connected through three rigid rods as to make triangle like structure. A gas containing such molecules performs 25 J of work when it expands at constant pressure. Heat given to gas is –
Five grams of helium having rms speed of molecules and of oxygen having rms of are introduced into a thermally isolated vessel. Find the rms speed of helium and oxygen individually when thermal equilibrium is attained. Neglect the heat capacity of the vessel.
If the temperature of moles of helium gas is increased by ., then the change in the internal energy of helium gas is
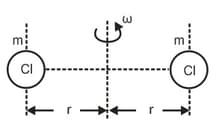
In a model of chlorine (), two atoms are rotated about their centre of mass as shown. Here the two '' atoms are apart and angular speed . If the molar mass of chlorine is , then the rotational kinetic energy of one molecule is
Find the temperature of the mixture, if two perfectly monoatomic gases at absolute temperatures and number of moles in the gases are and , respectively are mixed. Assume no loss of energy
If at a pressure of , mole of nitrogen occupies volume, then calculate the average energy of nitrogen molecules in
(Given : Avogadro's number = )
