Pressure of an Ideal Gas
Pressure of an Ideal Gas: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Avogadro's Number, Pressure inside Gas, Pressure Equation, Forms of Gas Pressure Equation & Temperature and Kinetic Energy etc.
Important Questions on Pressure of an Ideal Gas
At constant pressure, which of the following is true?
Kinetic energy per unit volume is . The pressure exerted by the gas is given by
atmospheric pressure is _____ in Pascals.
Which of the following shows the correct relationship between the pressure 'P' and density of an ideal gas at constant temperature ?
When the temperature of a gas is increased :
For a ideal gas, the kinetic energy is at a temperature of . What will be the kinetic energy if the temperature is raised to ?
Suppose there are molecules each of mass of an ideal gas in a container. The component of velocity of a molecule is denoted by . The gas is enclosed using a horizontal piston of area . If the temperature of gas is doubled keeping volume constant, we know from the gas law that the pressure will be doubled. On microscopic level this increase in pressure is because

Suppose there are molecules each of mass , of an ideal gas in a container. The component of velocity of a molecule is denoted by . The gas is enclosed using a horizontal piston of area . The pressure of the gas can also be written in terms of momentum transferred per collision and collision frequency on the wall of area as
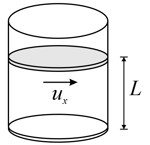
Suppose there are molecules each of mass , of an ideal gas in a container. The component of velocity of a molecule is denoted by . The gas is enclosed using a horizontal piston of area . The pressure of the gas is
The average kinetic energy of the molecule in a substance is directly proportional to its temperature.
Gas at pressure is contained in a vessel. If the mass of all the molecules are halved and their speed is doubled then the resulting pressure becomes . What is the value of ' '.
The pressure and the kinetic energy density of an ideal molecular gas is numerically related as:
The pressure exerted by an ideal gas on the walls of a container is
Assuming the expression of the pressure exerted by the gas on the walls of the container, it can be shown that pressure is
A flask contains argon and chlorine in the ratio of 2 : 1 by mass. The temperature of the mixture is . The ratio of average kinetic energies of two gases per molecule is
A flask contains argon and chlorine in the ration of 2 : 1 by mass. The temperature of the mixture is . The ratio of average kinetic energies of two gases per molecule is
The neutral temperature of is constant for a Cu - Fe thermocouple. When the cold junction is at , the value of inversion temperature is , but if the cold junction is at , the inversion temperature will be .................
Which of the following graphs best represents the relationship between absolute temperature of a gas and the average kinetic energy of the gas molecules?
If at the same temperature and pressure, the densities of two diatomic gases are respectively, the ratio of mean kinetic energy per molecule of gases will be
Assertion: The total translational kinetic energy of all the molecules of a given mass of an ideal gas is times the product of its pressure and its volume.
Reason: The molecules of a gas collide with each other and the velocities of the molecules change due to the collision.
