Conduction
Conduction: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Thermal Conduction, The Steady State Heat Flow, Appropriate Building Material for House & Appropriate Building Material for Nuclear Reactor etc.
Important Questions on Conduction
A metal rod of length has cross sectional areas and as shown in the figure. The ends are maintained at temperatures and . The temperature at middle point is___.
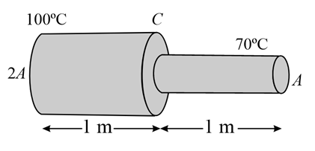
The end of a rod of length is maintained at and the end at . What is the temperature (in ) at a distance of from the end ?
What kind of building materials is appropriate for thermal conductivity?
What quality is required for the ppropriate Building Material for Nuclear Reactor ?
Heat transfer critical in nuclear reactors as Nuclear fission is heavily _____ reaction.
Heat transfer is critical for Nuclear reactors as nuclear fission is heavily exothermic reaction.
Why is heat transfer critical in nuclear reactors?
One end of a copper rod of length and area of cross-section is immersed in boiling water and the other end in ice. If the coefficient of thermal conductivity of copper is cal and the latent heat of ice is then the amount of ice which will melt (in grams) in one minute is
One end of the copper rod of uniform cross-section and length is kept in contact with ice and other end with water at . At the distance '' (in meter) from water along its length a temperature of is maintained so that in steady-state, the mass of ice melting is equal to that of the steam produced in the same time interval. Write the value of .
(Assume that the whole system is insulated from its surroundings. Latent heat of fusion of ice and vaporization of water are and , respectively.
If the transmission of heat takes through molecular collisions, it is called
People prefer to give a layer of ____ on the ceiling so that heat transfer is prohibited and keeps the room cooler.
What should be done to prevent the transfer of heat through concrete roof during hot summer days?
What role does a layer of earth or foam provide on a house having a concrete ceiling during summer days?
Why do the houses made of concrete roof gets very hot during summer days?
In steady state heat conduction, the equations that determine the heat current [heat flowing per unit time per unit area] and temperature in space are exactly the same as those governing the electric field and electrostatic potential with the equivalence given in the table below.
| Heat flow | Electrostatics |
Heat is passed through two cylindrical rods of same material. Their diameters and lengths are in the ratio and respectively. If their ends are maintained at same temperature difference, the ratio of rate of flow of heat through them is
What is the rate of flow of heat through a tapering rod of length tapering from radius and when the temperature of the ends are and and coefficient of thermal conductivity is
An icebox almost completely filled with ice at is dipped into a large volume of water at . The box has walls of surface area , thickness and thermal conductivity . Calculate the rate at which the ice melts in the box. Latent heat of fusion of ice .
Water is boiled in a container having a bottom of surface area , thickness and thermal conductivity . of water is converted into steam in the steady-state after the boiling starts. Assuming that no heat is lost to the atmosphere, calculate the temperature of the lower surface of the bottom. Latent heat of vaporization of water .
The normal body-temperature of a person is . Calculate the rate at which heat is flowing out of his body through the clothes assuming the following values. Room temperature , surface of the body under clothes , conductivity of the cloth, thickness of the cloth
