Heat Transfer
Heat Transfer: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as heat transfer, thermal conduction, coefficient of thermal conductivity, thermal resistance to heat flow, and thermal convection.
Important Questions on Heat Transfer
In summer water kept in a bottle become hot but when cover the bottle with a wet towel the water becomes cool. Why?
Two rods, one made of copper and the other made of steel of same length and same cross-sectional area are joined together. The thermal conductivity of copper and steel are and respectively. The free ends of copper and steel are held at and respectively. Calculate the temperature at the junction.
When of ice at is mixed with of water at in a container, the resulting temperature is
A solid iron sphere and a hollow iron sphere, both have the same mass and are at the same temperature. When placed in a colder surrounding, the heat loss per unit time will be
A metal vessel of negligible heat capacity contains of water (of specific heat capacity ). It is heated from to by immersion heater in. The average loss of heat in watts to the surroundings from the vessel during this time is nearly:
Why is the mode of heat transfer in Mercury is by conduction although it is a liquid?
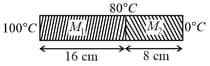
Two metallic blocks and of same area of cross-section are connected to each other (as shown in figure). If the thermal conductivity of is then the thermal conductivity of will be : [Assume steady state heat conduction]
Four semicircular rod of cross section area , radius , thermal conductivity '' are connected as shown then thermal resistance of configuration across point and is:
Is steel is a good conductor of heat?
A composite cylinder is made by two materials having thermal conductivities and as shown. Temperature of the two flat faces of cylinder are maintained at and
The end of a rod of length is maintained at and the end at . What is the temperature (in ) at a distance of from the end ?
A room has a concrete roof . At some instant, the temperature outside is and that inside is . If the bricks of thickness are laid down on the roof. Calculate the rate of heat flow under the same temperature condition (neglect convection).
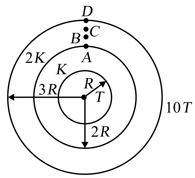
A composite spherical shell is made up of two materials having thermal conductivities and respectively as shown in the figure. The temperature at the inner most surface is maintained at whereas the temperature at the outer most surface is maintained at and are four points in the outer material such that . The net rate of heat flow from the outermost surface to the innermost surface of the shell will be (Neglect any radiation)
Many species cool themselves by sweating, because as the sweat evaporates, heat is given to the surroundings. A person exercising strenuously has an evaporative heat loss rate of about . If this person exercises strenuously for , how much water (in gm) must he drink to replenish his fluid loss? The heat of vaporization of water is at normal skin temperature. (Take: )
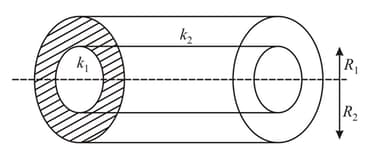
Inner surface of a cylindrical shell of length and of material of thermal conductivity is kept at constant temperature and the outer surface of the cylinder is kept at constant temperature such that as shown in figure. Heat flows from inner surface to outer surface to outer surface radially outward. Inner and outer radii of the shell are and respectively. Due to lack of space this cylinder has to be replaced by a smaller cylinder of length inner and outer radii and respectively and thermal conductivity of material . If rate of radially outward heat flow remains same for same temperature of inner and outer surface i.e. and , then find the value of .
List the applications of thermal conductivity.
What are the applications of thermal convection?
Two different materials of equal dimensions (length and uniform cross-sectional area ) having thermal conductivities and respectively are connected together through a bolt . The bolt (length , area ) is of another material with thermal conductivity such that . The left sides of the material and are kept at the temperature whereas the right sides of the material and are kept at the temperature as shown in the figure below such that . Assume that the bolt is thermally insulated from materials and . The equivalent thermal resistance of this system is
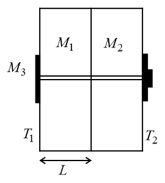
Explain the cooling of Transformer based on thermal convection.
Explain thermal convection along with the applications of convection in daily life.
