Principle of Calorimetry
Principle of Calorimetry: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Units of Heat, Calorimetry, Mechanical Equivalent of Heat, Principle of Calorimetry, Mixing of Liquids at Different Temperatures, and Calorimeter.
Important Questions on Principle of Calorimetry
Initially, a beaker has of water at temperature . Later another of water at temperature was poured into the beaker. The temperature, of the water after mixing is
Initially, a beaker has of water at temperature . Later another of water at temperature was poured into the beaker. The temperature, of the water after mixing is
Calorie is the unit of which physical quantity?
Calorie is the unit of which physical quantity?
SI unit of heat is kelvin and SI unit of temperature is joule.
What is the SI unit of heat?
One calorie is nearly equal to _____ .
A heater supplying constant power watts is switched ON at time to raise the temperature of a liquid kept in a calorimeter of negligible heat capacity. A student records the temperature of the liquid at equal time intervals. A graph is plotted with on the -axis versus on the -axis. Assume that there is no heat loss to the surroundings during heating. Then,
Steam at is passed into of water contained in a calorimeter at till the temperature of water and calorimeter is increased to . The mass of the stean condensed is nearly
(Water equivalent of calorimeter Specific heat of water Latent heat of vapourisation )
Two tank and contain water at and respectively. The amount of water that must be taken from and to prepare of water at
Match the Column (A) and Column (B)
Column (A) Column (B)
a. The heating of a body takes place by conduction
b. Heat transfer in solid b. Its volume expands
c. of steel heat c. Measured by thermometer
d On heating the solid d. The substance has a property
e specific heat y. is a good conductor.
The whole mixture in the calorimeter become ice if:
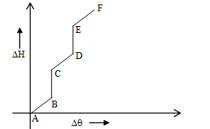
A solid is heated up and vs (Heat given, change in temperature) is plotted as shown in figure. Material exist in only one phase in-
of ice at is kept in a large container of negligible heat capacity of steam at is passed over the container. The final temp of mixture when thermal equilibrium is attained:
[Specific Heat of ice
Specific Heat of steam
Latent Heat of fusion
Latent Heat of vaporizationof steam at is added toof water at in a container of negligible mass. Assuming no heat is lost to the surrounding, the mass of water in the container at thermal equilibrium is (Latent heat of vaporisation, specific heat of water)
ice at is mixed with water at in an insulating vessel having negligible heat capacity. Calculate the final mass of water remaining in the container.
Given: specific heat of water
Specific heat of ice
Latent heat of fusion of ice
Water of volume in a container is heated with a coil of power at . The lid of the container is open and energy dissipates at rate of . In how much time temperature will rise from to ? [Given specific heat of water is ]
of water at is poured on a large block of ice at . The mass of ice that melts is:
Liquids and are at and , respectively. When mixed in equal masses, the temperature of the mixture is found to be , The specific heats of and are in the ratio of , where and are integers, then find the minimum value of .