Specific Heat Capacity
Specific Heat Capacity: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Specific Heat Capacity of Water, Heat Capacity, Specific Heat Capacity, Molar Specific Heat Capacity & Variation of Specific Heat Capacity of Water with Temperature etc.
Important Questions on Specific Heat Capacity
The molar heat capacity of water at constant pressure is . When 1kJ of heat is supplied to 100g of water, which is free to expand, the increase in temperature of water is
Two different liquids of same mass are kept in two identical vessel, which are placed in a freezer that extracts heat from them at the same rate causing each liquid to transform into a solid. The schematic figure below shows the temperaure vs time plot for the two materials. We denote the specific heat in the liquid states to be and for materials and respectively, and latent heats of fusion and respectively.
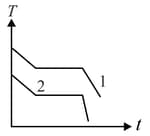
Choose the correct option.
200 g water is heated from to . Ignoring the slight expansion of water, the change in its internal energy is close to (Given specific heat of water J/kg/K):
Water is used as a coolant because
A person weighing takes in diet per day. If this energy were to be used in heating the body of person without any losses, then the rise in his temperature is (specific heat of human body )
Amongst object A and B, if the specific heat of object A is less than of object B, then
The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of mass of water through is called its
The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of mass of water through is called its
Specific heat of a substance is given by , find out amount of heat required to raise the temperature of substance from to
The number of degrees of freedom of a gas whose specific heat capacity at constant pressure is is
(universal gas constant )
ice at is mixed with steam at . The minimum value of so that finally all ice and steam converts into water is,
(Use, , (melting) and (vaporization).)
Which statement is false for specific heat of water?
During illness an man ran a fever of instead of normal body temperature of Assuming that the human body is mostly water, how much heat is required to raise his temperature by that amount?
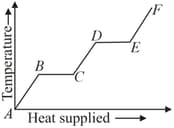
A source of heat supplies heat at a constant rate to a solid cube. The slope of portion of the graphs gives :-
Calculate the change of heat when of water at is heated to ? (specific heat of water )
In a mixture of two gases, we have mole of a certain gas having and mole of another gas having . Calculate the value of for the given mixture of gases.
It is known that the universal gas constant is times (molar heat capacity at constant pressure) for an ideal monatomic gas. What is the value of here?
The temperature of moles of a gas is changed from to under isochoric process and internal energy is changed by The of the gas is
What is the significance of infinite heat capacity of a substance?
Water is used as a coolant because
