Heat, Internal Energy and Work
Heat, Internal Energy and Work: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Internal Energy, Work Done by Thermodynamic System, Internal Energy in Thermodynamics & Distinction between Heat and Internal Energy etc.
Important Questions on Heat, Internal Energy and Work
An ideal is filled in a closed, rigid and thermally-insulated container. A coil of resistance and carrying a current of supplies heaT to the gas. The change in the internal energy of the gas after minutes will be:
For an ideal gas, its internal energy is the function of its:
Write the difference between.heat and internal energy
Heat and internal energy are path function
Define internal energy and heat?
A gas mixture consists of moles of and moles of at temperature . Neglecting all vibrational modes, the total internal energy of the system is . Find the value of .
A thermally insulated vessel with nitrogen gas at is moving with a velocity of . If the vessel is stopped suddenly, the percentage change in the pressure of the gas is nearly (Assume entire loss in of the gas is given as heat to gas and )
An ideal gas has initial volume and is kept in a vessel. It undergoes a change and follows the following relation (where is pressure, and is volume). Find the change in internal energy of the gas if its final pressure is .
Heat transferred to the surrounding will increase the internal energy of a system.
The standard internal energy change of the cell reaction will be
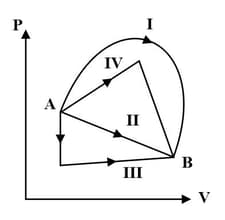
A thermodynamical system undergoes cyclic process as shown in figure. Work done by the system is _____ (in letters).
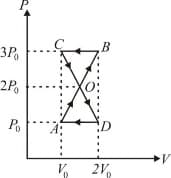
An ideal gas undergoing a change of state from to through four different paths, and as shown in the diagram that lead to the same change of state, then the change in internal energy is same in all the cases.
A gas expands from a volume of to a volume of against an external pressure of . The work done by the gas will be
Calculate the magnitude of work done (in joules) when mole of an ideal gas at expands isothermally and reversibly from an initial volume of litres to the final volume of litres.
Calculate the work done (in joules) when of an ideal gas at expands isothermally and reversibly from initial volume of litres to the
final volume of litres
A gas expands from a volume of 1 m3 to a volume of 2 m3 against an external pressure of 105 N m-2 . The work done by the gas will be
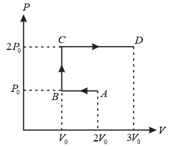
Calculate the work done by an ideal gas in the thermodynamic process depicted in the adjoining graph.
Which is contained in a body in a greater amount: heat or internal energy?
The internal energy of a system in any spontaneous process always tends to decrease.
Heat transferred to the surrounding will increase the internal energy of a system.