Second Law of Thermodynamics
Second Law of Thermodynamics: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Second Law of Thermodynamics, Terms in Second Law of Thermodynamics, Engines and Cyclic Process & Entropy of Thermodynamic System etc.
Important Questions on Second Law of Thermodynamics
Given the following entropy values at 298 K and 1 atm : The entropy change for the reaction
An engine operating between the boiling and freezing points of water will have
A. Efficiency more than .
B. Efficiency less than the efficiency of a Carnot engine operating between the same two temperatures.
C. Efficiency equal to .
D. Efficiency less than .
Choose the correct answer from the options given below
A flask containing at . and was connected to a flask containing gas at and . The gases were allowed to mix isothermally, determine the entropy change for the system:
For an increase in the entropy define ____ of nature.
Which of the following option are correct for the second law of thermodynamics?
The cause of irreversibility of a natural process is:
Causes of irreversible process.
Heat cannot by itself flow from a body at lower temperature to a body at higher temperature” is a statement or consequence of
Mention the causes for irreversibility of a process.
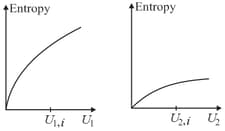
Graphs below show the entropy versus energy of two systems and at constant volume. The initial energies of the systems are indicated by and respectively. Graphs are drawn to the same scale. The systems are then brought into thermal contact with each other. Assume that, at all times the combined energy of the two systems remains constant. Choose the most appropriate option indicating the energies of the two systems and the total entropy after they achieve the equilibrium.
When of ice at melts to water at , the resulting change in its entropy, taking latent heat of ice to be , is,
The change in entropy when a ice cube at is transformed into water at in is
Take ,
Clausius's statement is a part of
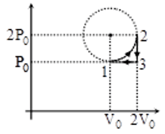
One mole of ideal monoatomic gas is taken along a cyclic process as shown in the figure. Process
1 → 2 shown is 1/4th part of a circle as shown by dotted line process 2 → 3 is isochoric while
3 → 1 is isobaric. If efficiency of the cycle is n% where n is an integer. Find n.
One mole of an ideal monatomic gas undergoes the following four reversible processes:
Step It is first compressed adiabatically from volume to
Step then expanded isothermally to volume
Step then expanded adiabatically to volume
Step then compressed isothermally to volume If the efficiency of the above cycle is then is
What is the entropy change in during the melting of 27.3 g of ice of ? (Latent heat of fusion of ice = 330 )
Choose the incorrect relation among these
According to the third law of thermodynamics which one of the following quantities for a perfectly crystalline solid is zero at absolute zero?
In the following a statement of Assertion is followed by a statement of Reason.
Assertion: During free expansion of an ideal gas, its entropy increases but work done by the gas is zero.
Reason: During free expansion, volume increases but temperature remains constant.