Specific Heat Capacity
Specific Heat Capacity: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Molar Specific Heat Capacities in Terms of Gas Constant, Molar Specific Heat Capacity at Constant Volume, Mayer's Relation, Molar Specific Heat Capacity at Constant Pressure, and Heat Capacity of Solids.
Important Questions on Specific Heat Capacity
At a given temperature, the specific heat of a gas at constant pressure is always greater than its specific heat at constant volume.
An insulated box containing a diatomic gas of molar mass is moving with velocity . The box is suddenly stopped. The resulting change in temperature is . What will be the value of ?
The specific heat capacity of water is less than that of steam.
The specific heat capacity of water is less than that of ice.
The specific heat capacity of water is less than that of aluminium.
Define molar specific heat capacity at constant volume and pressure.
A container has 4.2 litres of water at . Heat required to boil water in is
The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of mass of water through is called its
Define heat capacity and write its unit.
A molecule of a gas has six degrees of freedom. Then, the molar specific heat of the gas at constant volume is
One gram mole of an ideal gas with the ratio of constant pressure and constant volume specific heats is mixed with gram moles of another ideal gas with . If the for the mixture is , then what will be the value of ?
How much heat energy (in ) is necessary to raise the temperature of of water from to ?
Specific heat of an ideal gas at constant volume and at constant pressure are related to universal gas constant are as
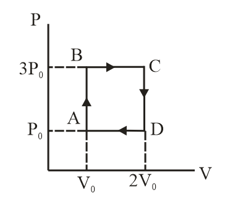
An ideal monatomic gas is carried along the cycle as shown in the figure. The total heat absorbed in this process is
How the change in specific heat of the water can be explained at low temperatures?
Which statement is false for specific heat of water?
A source of heat supplies heat at a constant rate to a solid cube. The slope of portion of the graphs gives :-
Calorie is defined as the amount of heat required to raise temperature of of water by and it is defined under which of the following conditions :-
For the next three questions
An ideal diatomic gas is expanded so that the amount of heat transferred to the gas is equal to the decrease in its internal energy.
The molar specific heat of the gas in this process is given by C whose value is
The energy in food is measured in _____. (Fahrenheit/ calorie/ Celsius/ metre)
