Thermodynamic Processes and Indicator Diagrams
Thermodynamic Processes and Indicator Diagrams: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Indicator Diagrams, Cyclic Process, Cyclic Process without Indicator Diagrams & Polytropic Process etc.
Important Questions on Thermodynamic Processes and Indicator Diagrams
A process in which the amount of heat supplied to the system goes fully to change its internal energy and temperature is
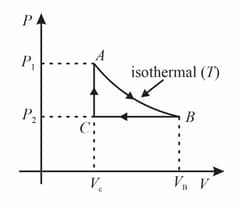
One mole of an ideal monoatomic gas undergoes the following four reversible processes:
Step 1 It is first compressed adiabatically from volume to .
Step 2 Then expanded isothermally at temperature to volume .
Step 3 Then expanded adiabatically to volume
Step 4 Then compressed isothermally at temperature to volume .
Then, is
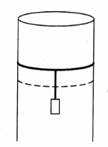
A long cylindrical pipe of radius is closed at its upper end and has an airtight piston of negligible mass as shown. When a mass is attached to the other end of the piston, it moves down. If the air in the enclosure is cooled from temperature to the piston moves back to its original position. Then is close to (Assuming air to be an ideal gas, atmospheric pressure is )
Which of the following statements about the diagram of an ideal gas of fixed number of particles is incorrect?
Quasi-static process is :
One mole of an ideal gas is taken around the complete cycle as shown in the PV-diagram. Considering the universal gas constant R, the work done by the gas in one complete cycle is:
From the given options, using which variables for X and Y -axis we can make an isotherm graph?
One mole of an ideal gas expands adiabatically at constant pressure such that its temperature The value of the adiabatic constant of gas is
One mole of an ideal monatomic gas is compressed isothermally in a rigid vessel to double its pressure at room temperature, . The magnitude of work done on the gas will be:
During adiabatic change, specific heat is
The given diagram shows four processes i.e., isochoric, isobaric, isothermal and adiabatic. The correct assignment of the processes, in the same order is given by: 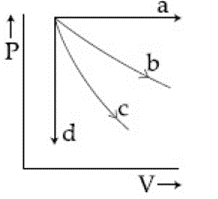
A thermodynamic system undergoes cyclic process as shown in the figure. The work done by the system is,
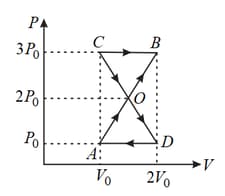
Find the amount of work done to increase the temperature of one mole of ideal gas by , if it is expanding under the condition .
A spherical bubble inside water has radius Take the pressure inside the bubble and the water pressure to be The bubble now gets compressed radially in an isothermal manner so that its radius become For the magnitude of work done in the process is given by where is a constant. Find
During an adiabatic expansion, a gas does of work against the surroundings. It is then cooled at constant volume by removing of energy from the gas. The magnitude of the total change in internal energy of the gas is . The value of is
The volume of a given mass of monatomic gas changes with temperature according to the relation The work done when temperature changes by will be The value of is ____________ . [R =universal gas constant]
A spherical bubble inside water has radius Take the pressure inside the bubble and the water pressure to be The bubble now gets compressed radially in an adiabatic manner so that its radius becomes For the magnitude of the work done in the process is given by where is a constant and The value of is
Consider one mole of helium gas enclosed in a container at initial pressure and volume It expands isothermally to volume After this, the gas expands adiabatically and its volume becomes The work done by the gas during isothermal and adiabatic expansion processes are and respectively. If the ratio then is
If an ideal diatomic gas follows the process as shown in graph, where is temperature in and is volume in , then molar heat capacity for this process will be [in terms of gas constant ],
For a reversible process, necessary condition is
