Bernoulli's Principle and Its Applications
Bernoulli's Principle and Its Applications: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Bernoulli's Theorem, Blowing-off of Rooftop in Wind Storm, Pressure Energy in Fluid Flow, Potential Energy in Fluid Flow, Kinetic Energy in Fluid Flow, and Derivation of Bernoulli’s Equation.
Important Questions on Bernoulli's Principle and Its Applications
A non-spinning ball is not subjected to the Magnus effect. This Magnus effect is equivalent to :
Which of the following forces are acting on a non-spinning ball during its flight:
Motion of ball without spin in air follow the path
If pressure on the ball at the top be and bottom be then for ball moving without spin
When the moves with spin in air then at its top and bottom part pressures are represented by and respectively then which of the following are correct.
Motion of ball with spin in air follow the path
Potential energy term of Bernoulli's equation is not considered for its application in:
The potential energy term in Bernoulli's equation is present due to:
Bernoulli's theorem is a restatement of :
Bernoulli's theorem is an explanation for which of the following human ailments :
Which of the following phenomenon can exaplain the blood flow in an artery and cause of heart attack?
Venturi meter work on
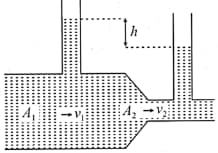
A liquid flows through a horizontal tube as shown in figure. The velocities of the liquid in the two sections, which have areas of cross-section and , are and , respectively. The difference in the levels of the liquid in the two vertical tubes is . Then
| A | B |
| Rocket propulsion | Bernoulli’s principal in fluid dynamics |
| Aeroplane | Total internal reflection of light |
| Optical fibers | Newton’s laws of motion |
| Fusion test reactor | Magnetic confinement of plasma |
| Photoelectric effects |
A tank is filled with water to a height H. A hole is punched in one of the walls at a depth h below the water surface. Then the distance x from the foot of the wall at which the stream strikes the floor is -
The glycerin of density is flowing through a conical tube with end radii and respectively. The pressure difference across the ends is . The rate of flow of glycerine through the tube is
If the velocity head of a stream of water is equal to , then its speed of flow is ()
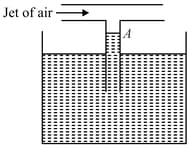
Water stands at level in the arrangement shown in the figure. What will happen if a jet of air is gently blown into the horizontal tube in the direction shown in the figure?
A river of salty water if flowing with a velocity . If the density of the water is , then the kinetic energy of each cubic meter of water is
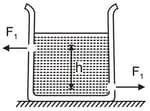
There are two identical small holes of an area of cross-section on the opposite sides of a tank containing a liquid of density . The difference in height between the holes is . Tank is resting on a smooth horizontal surface. The horizontal force which will have to be applied on the tank to keep it in equilibrium is