Stokes Law
Stokes Law: Overview
This topic contains concepts like Viscous Force on Spherical Bodies, Stokes Law, Velocity of Spherical Ball in Viscous Medium and Terminal Velocity of Spherical Ball.
Important Questions on Stokes Law
Rain drops falling under gravity do not acquire very high velocity. Why?
The constant velocity of the raindrop is because of _____.
A raindrop falling in air is similar to motion of what kind of body in viscous medium?
Falling rain drops velocity vary with the height with respect to the surface.
Stoke's can be applied for the measurement of the viscosity of fluids
List the applications of Stokes Law.
A drop of water of radius is falling in air. If the coefficient of viscosity of air is , the terminal velocity of the drop will be: (The density of water and )
Eight drops of water, each of radius are falling through air at a terminal velocity of . If they coalesce to from a single drop, then the terminal velocity of combined drop will be:
A metallic sphere of mass falls through glycerine, If we drop a ball of mass of same metal into a column of glycerine, the terminal velocity of the ball will be
A spherical ball of radius is falling in a viscous fluid with velocity . The retarding viscous force acting on the spherical ball is:
A rain drop of radius has a terminal velocity in air The viscosity of air is poise. Find the viscous force on the rain drops.
Two rain drops reach the earth with the terminal velocities in the ratio . The ratio of radii is :
The velocity of a small ball of mass M and density when dropped in a container filled with glycerine becomes constant after some time. If the density of glycerine is , the viscous force acting on the ball is
The velocity of a small ball of mass M and density when dropped in a container filled with glycerine becomes constant after some time. If the density of glycerine is , the viscous force acting on the ball is
A sphere of radius is gently dropped into liquid of viscosity ɳ in a vertical uniform tube. It attains a terminal velocity . Another sphere of radius when dropped into the same liquid, will attains its terminal velocity
What is velocity of a metallic ball of radius falling in a tank of liquid at the instant when its acceleration is one-half that of the freely falling body?
(The densities of metal and of liquid are and respectively, and the viscosity of the liquid is ɳ)
A small tiny lead shot is gently dropped on the surface of a viscous liquid then:
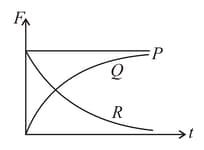
A spherical ball is dropped in a long column of viscous liquid. Which of the following graphs represent the variation of
(i)gravitational force with time
(ii) viscous force with time
(iii) net force acting on the ball with time?
The viscous force acting on a rain drop of radius 0.35 mm falling through air with a velocity of , is
What is velocity of a metallic ball of radius falling in a tank of liquid at the instant when its acceleration is one-half that of the freely falling body?
(The densities of metal and of liquid are and respectively, and the viscosity of the liquid is ɳ)
