Streamline Flow
Streamline Flow: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Types of Fluid Flow, Steady Flow of Fluid, Streamline Flow, Laminar Flow, Turbulent Flow, Equation of Continuity, Condition for Start of Turbulence, and Properties of Streamline.
Important Questions on Streamline Flow
A common application of laminar flow is in the smooth flow of a viscous liquid through a tube or pipe.
What is streamline? What are its properties?
The laminar flow of a fluid can be described as the flow of parallel streamlines.
In laminar flow of a fluid:
Here we know that for turbulent flow, we need a certain limit of Reynolds number. So, what is Reynold's number?
Rather than higher velocity of the flow, starting the turbulent is depends on _____.
For starting turbulent, we need low velocity flow.
What is reynolds number condition for starting the turbulent?
Streamline flow is more likely for liquids with _____ (low density/high density) and high viscosity.
Stream line flow of a liquid at a given point.
Water is moving with a speed of through a pipe with a cross-sectional area of . The water gradually descends as the pipe increases in area to . The speed of flow at the lower level is
A stream of water flowing horizontally with a speed of gushes out of a tube of cross-sectional area and hits a vertical wall normally. Assuming that it does not rebound from the wall, the force exerted on the wall by the impact of water is:
A container has a hole at the bottom of area Liquid is being added at the rate into it so that height of liquid in container remains constant. The height of liquid in container at equilibrium is
Water is flowing through a tube of non-uniform cross-section. If the radii of the tube at the entrance and exit are in the ratio , then the ratio of the velocity of liquid entering and leaving the tube is
Blood is flowing at the rate of in a capillary of cross-sectional area . The velocity of flow is
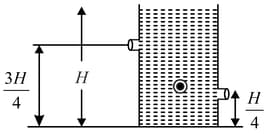
A massless container is filled with liquid of density . It contains two holes as shown in figure. Container rests on ground. Area of the two holes are each. Container is filled with liquid upto height . Then -
Water is flowing in a pipe of diameter 4 cm with a velocity . The water then enters in to a pipe of diameter 2 cm. the velocity of water in the other pipe is
Water is moving with a speed of through a pipe with a cross-sectional area of . The water gradually descends as the pipe increases in area to . The speed of flow at the lower level is
