Centre of Mass Frame
Centre of Mass Frame: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Centre of Mass and Centre of Mass Frame & Application of Centre of Mass Frame of Reference etc.
Important Questions on Centre of Mass Frame
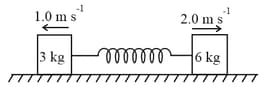
Calculate the maximum extension of the spring of spring constant , initially the spring is unstretched, when the two blocks of mass and respectively are placed on a smooth horizontal surface, and they are given velocities as shown in the figure
A plank is moving in a horizontal direction with a constant acceleration . A uniform rough cubical block of side rests on the plank and is at rest relative to the plank.
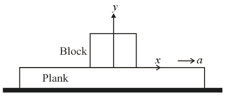
Let the centre of mass of the block be at at a given instant. If , then the normal reaction exerted by the plank on the block at that instant acts at
Consider a two block system having masses and , as shown in the figure. If block A is pushed towards the centre of mass through a distance , by what distance should the block be moved so as to keep the centre of mass at the same position.

A uniform semi-ring of radius meter is rotating about one of its corners on a frictionless horizontal table. The plane of motion is the same as that of the semi-ring. The hinge (origin) is suddenly removed. Find the co-ordinates (in ) of point after removing the hinge.
A body of mass moving with a velocity is approaching a second body of same mass but at rest. The total kinetic energy of the two bodies with respect to centre of mass frame is:
A stationary pulley carries a rope one end of which supports a ladder with a man and the other a counterweight of mass . The man of mass climbs up a distance with respect to the ladder and then stops. The displacement of the centre of mass of this system is
A man of mass stands at one end of a plank of length which lies at rest on a frictionless surface. The man walks to the other end of the plank. If the mass of the plank is , the distance that the man moves relative to the ground is
A man weighing is standing in a trolley weighing . The trolley is resting on frictionless horizontal rails. If the man starts walking on the trolley with a speed of , then after , his displacement relative to the ground will be
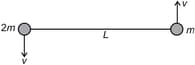
Two particles of masses and are connected by a string of length and placed at rest over a smooth horizontal surface. The particles are then given velocities as indicated in the figure shown. The tension developed in the string will be
A thick straight wire of length is fixed at its midpoint and then bent in the form of a circle. The shift in its center of mass is
Two blocks and of masses and respectively are attached at opposite ends of a spring of constant and is placed on a smooth horizontal surface. Spring is initially at its natural length . is given a velocity and given velocity as shown.
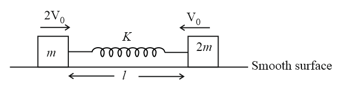
Maximum separation between and centre of mass of the system will be:
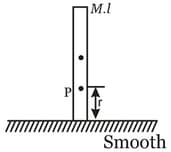
A rod of mass m and length is placed vertically on a horizontal smooth surface. A small disturbance is given at lowest end in horizontal direction. The locus of a point P which is at a distance r on the rod from lowest point of the rod will be a/an