Variable Mass System
Variable Mass System: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Variable Mass System and Theory of Rocket Propulsion.
Important Questions on Variable Mass System
A 600 kg rocket is set for a vertical firing. If the exhaust speed is 1000 the mass of the gas ejected per second to supply the thrust needed to overcome the weight of rocket is :
If the force on a rocket moving with a velocity of is , then the rate of combustion of the fuel is:
The difference between the working of a jet and a rocket is
A jet engine works on the principle of
The rate of mass of the gas emitted from rear of a rocket is initially . If the speed of the gas relative to the rocket is and mass of the rocket is , then the acceleration of the rocket (in ) is
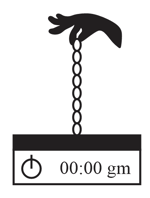
A jeweler is holding a gold chain of uniform mass per unit length hanging vertically just above a weighing scale as shown in the figure. He offers to charge the customer for half of the maximum reading of the scale, after he releases the chain. What percentage more than the actual price does the customer pay if he agrees to the offer?
The difference between the working of a jet and a rocket is
A jet engine works on the principle of
The rate of mass of the gas emitted from rear of a rocket is initially . If the speed of the gas relative to the rocket is and mass of the rocket is , then the acceleration of the rocket (in ) is
A rocket of initial mass ejects gases at a constant rate of with constant relative speed of . What is the acceleration of the rocket one minute after the blast?
If the force on a rocket, which ejects mass at a speed relative the rocket is , due to combustion of the fuel, then the rate of combustion of the fuel is
A rocket has a mass of , of this is fuel. It ejects fuel vapours at the rate of with a velocity of relative to the rocket. It is supposed that the rocket is outside the gravitational field. The initial up thrust on rocket when it just starts moving upwards.
A rocket with a lift-off mass is blasted upward with an initial acceleration of . If , then the initial thrust of the blast is
A rocket standing vertically on a launch pad has to start moving up with practically zero velocity. If the initial mass of the rocket is kg, then the rate of burning of the fuel should be [Take and velocity of exhaust gases = 10 ]
Steady rain, giving an hour, turns suddenly into a downpour giving an hour and the speed of the rain drops falling vertically on to a flat roof simultaneously doubles. The pressure exerted by the falling rain on the roof is raised by a factor of
An open carriage in a goods train is moving with a uniform velocity of . If the rain adds water with zero velocity at the rate of , then the additional force applied by the engine to maintain the same velocity of the train is
The rate of the mass of the gas emitted from rear of a rocket is initially . If the speed of the gas relative to the rocket is and mass of the rocket is , then the acceleration of the rocket (in is
Diwali rockets are ejecting of gases per second at a velocity of. The accelerating force on the rocket will be
A rocket with a lift-off mass kg is blasted upward with an initial acceleration of . Then the initial thrust of the blast is
At a certain instant of time, the mass of rocket going up vertically is . If it is ejecting of gas per second at a speed of , the acceleration of the rocket would be (Taking )
