Elastic Potential Energy
Elastic Potential Energy: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Potential Energy of a Stretched Wire, Elastic Potential Energy per Unit Volume of Wire, Calculation of Maximum Height of Mountain on Earth & Spring Analog in Hooke's Law etc.
Important Questions on Elastic Potential Energy
Which of the given metal is not using for making rope for the crane?
The buckling of a beam is found to be more if:
A rod elongates by when a body of mass is suspended from it. The work done is
is the force constant of a spring. The work done in increasing its extension from to will be
A work of is done on a wire of length and area of cross-section . If the Young's modulus of the material of the wire is , then the wire must be
When a steel wire fixed at one end is pulled by a constant force at its other end, its length increases by . Which of the following statements is not correct?
When an elastic material with Young's modulus is subjected to a stretching stress the elastic energy stored per unit volume of the material is
Which of the following expressions can be used to calculate the maximum height of mountains on earth?
The ratio of elastic potential energy per unit volume for two wires made out of same material and having same length but diameter in the ratio , when stretched by the same load is:
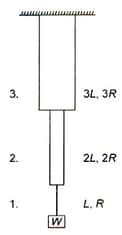
Lengths and radii of three wires of the same material (Young's modulus ), respectively which are joined end to end with weight is suspended as shown below. Find the elastic potential energy of the system neglecting the self-weight.
A catapult is made of rubber cord which is 42 cm long, with 6 m m diameter of cross-section and of negligble mass. The boy keeps a stone weighing 0.02 kg on it and stretches the cord by 20 cm by applying a constant force. When released, the stone flies off with a velocity of . Neglect the change in the area of crose-section of the cord while stretched. The Young's modulus of rubber is approx:
A uniform rod of length is acted upon by a force in a gravity-free region, as shown in the figure. If the area of cross-section of the rod is and it's Young's modulus is , then the elastic potential energy stored in the rod due to elongation is
When the load on a wire is increased from to the elongation increases from to . The required work done during the extension of the wire is
An elastic string of length and cross section area is attached between two pegs at a distance of . A particle of mass is kept at mid point of string and stretched by and released. As string attains natural length, the particle attains a speed . Then young’s modulus of string is of order
Work done for a certain spring when stretched through 1 mm is 10 joule. The amount of work that must be done on the spring to stretch it further by 1 mm is
One end of a slack wire (Young's modulus, , length, and cross-sectional area, ) is clamped to a rigid wall and the other end to a block (mass ) which rests on a smooth horizontal plane. The block is set in motion with a speed, . What is the maximum distance the block will travel after the wire becomes taut?
Two wires of the same material and length but diameters in the ratio 1 : 2 are stretched by the same force. The elastic potential energy per unit volume for the wires, when stretched by the same force will be in the ratio.
Consider four steel wires of dimensions given below (d = dimeter and l = length):
I.
II.
III.
IV.
If same force is applied to all the wires then the elastic potential energy stored will be maximum in wire.
A wire fixed at the upper end stretches by length, by applying a force, . What is the work done in stretching the wire?
In a wire stretched by hanging a weight from its end, the elastic potential energy per unit volume in terms of longitudinal strain and modulus of elasticity is -