Equation of Continuity
Equation of Continuity: Overview
This topic covers the concept of Equation of Continuity.
Important Questions on Equation of Continuity
A laminar stream is flowing vertically down from a tap of cross-section area 1 cm2. At a distance 10 below the tap, the cross-section area of the stream has reduced to 1/2 cm2. Find the volumetric flow rate of water from the tap
A cylindrical vessel open at the top is 20 cm high and 10 cm in diameter. A circular hole whose cross-sectional area 1cm2 is cut at the centre of the bottom of the vessel. Water flows from a tube above it into the vessel at the rate 100 cm3 s-1 . Find the height of water in the vessel under steady state.
Water is moving with a speed of through a pipe with a cross-sectional area of . The water gradually descends as the pipe increases in area to . The speed of flow at the lower level is
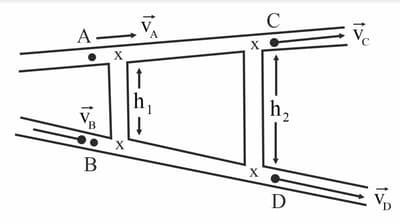
An ideal fluid is flowing in two pipes of the same cross-sectional pipe area. Both the pipes are connected with two vertical tubes, of length h1 and h2 as shown in the figure. The flow is streamline in both pipes. If the velocity of the fluid at A, B, and C are , , and respectively, the velocity of the fluid at (in m/s) is -
The cylindrical tube of a spray pump has a cross-section of 8.0 cm2 one end of which has 40 fine holes each of diameter 1.0 mm. If the liquid flow inside the tube is 1.5 m/min, what is the speed of ejection of the liquid through the holes?
A horizontal pipe has a cross-section of in one region and of in another. The water velocity at the first is and the pressure in the second is . The pressure of water in region is given by . Then the value of is.
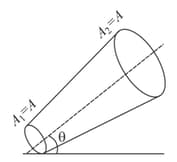
A portion of a tube is shown in the figure. Fluid is flowing from cross-section area to . The two cross-sections are at distance from each other. The velocity of the fluid at section is . If the pressures at are same, then the angle made by the tube with the horizontal will be
Mumbai needs of water annually. Its effective surface area is and it receives an average rainfall of annually. If of this rain water is conserved, it will meet approximately
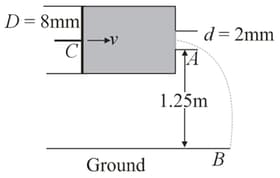
Consider a horizontally oriented syringe containing water located of a height of above the ground. The diameter of plunger is and the diameter of the nozzle is . The plunger is pushed with a constant speed of . Find the horizontal range of water stream on the ground. Take .
Water is moving with a speed of through a pipe with a cross-sectional area of . The water gradually descends as the pipe increases in area to . The speed of flow at the lower level is
Among of the following figures shown below, the correct one regarding the steady flow of a non-viscous liquid is
The wind flows at a velocity perpendicular to the blades of a windmill which sweep out a circle of area . If the density of the air is , find the mass of the air passing through blades of a windmill in time :
A tank is filled with the help of a cylindrical tube of area of cross-section A at a constant speed . The tank has a hole of area at bottom. Level of water in the tank will not go up beyond (take )
The ratio of the cross- sectional radius at entry and exit end of a pipe of non uniform cross-section is .Water is flowing through this pipe.Then the ratio of velocities of water at entry and exit end of pipe is:
Statement 1: A water stream falls from a tap becomes narrower as it falls.
Statement 2: The velocity of water increases as it falls.
Water is flowing through a channel of width with a speed of . The water then flows into four identical channels of width of each. The depth of the water does not change as it flows into the four identical channels. Find the speed of the water in one of the smaller channel?
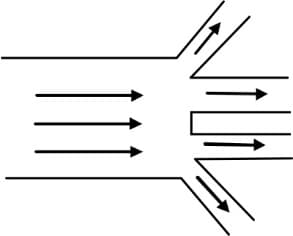
Consider an incompressible liquid flowing through a horizontal tube as shown in the figure. Then the velocity of the fluid in one of the sections of the tube as shown is:
Blood is flow rate through a capillary of cross-sectional area of is . The velocity of flow of blood is -
Water flows in a horizontal tube (see figure). The pressure of water changes by between and where the area of cross-sections are and respectively. What is the volume flow rate of water through the tube. (density of water )
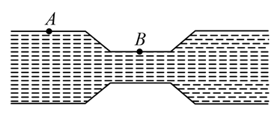
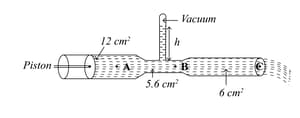
A glass tube has three different cross sectional areas with the values indicated in the figure. A piston at the left end of the tube exerts pressure so that the mercury within the tube flows from the right end with a speed of . Three points within the tube are labeled and . The atmospheric pressure is ; and the density of mercury is (use ):