Static Friction
Static Friction: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Static Friction, Dependence of Static Friction Force on Various Factors, Limiting Friction Force, and Coefficient of Static Friction.
Important Questions on Static Friction
Consider a car moving along a straight horizontal road with speed of . If the coefficient of static friction between the tyres and the road is , the shortest distance in which the car can be stopped is (taking )
A heavy uniform chain lies on a horizontal table-top. If the coefficient of friction between the chain and the table surface is , then the maximum fraction of the length of the chain that can hang over one edge of the table is
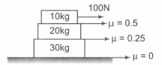
The coefficient of static friction, between block of mass and the table as shown in the figure is . The maximum mass value of block so that the two blocks do not move is (The string and the pulley are assumed to be smooth and massless
A block of mass rests on a rough inclined plane making an angle of with the horizontal. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the plane is The frictional force on the block is
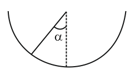
An insect crawls up a hemispherical surface very slowly (see the figure). The coefficient of friction between the insect and the surface is . If the line joining the center of the hemispherical surface to the insect makes an angle with the vertical, the maximum possible value of is given by,
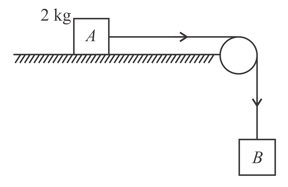
A block of mass lies on a horizontal surface in a truck. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the surface is . If the acceleration of the truck is . Find the frictional force acting on the block.
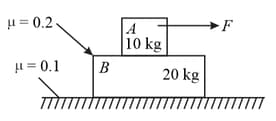
A block with mass is resting on another block of mass As shown in figure, a horizontal rope tied to a wall holds it. The coefficient of friction between and is while coefficient of friction between and the ground is The minimum required force to start moving will be
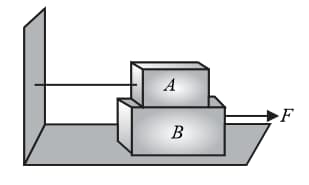
Consider the situation shown in the figure. The wall is smooth but the surfaces of blocks and in contact are rough. The friction on due to in equilibrium
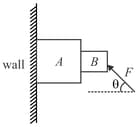
Consider the system shown in the figure. The wall is smooth, but the surfaces of blocks and in contact are rough. The friction on due to in equilibrium is
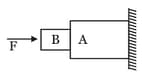
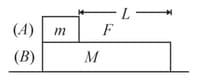
In the given diagram, what is the minimum value of horizontal external force on block so that block slides on the ground?
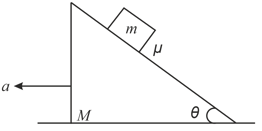
A block of mass is at rest relative to a stationary wedge of mass . The coefficient of friction between the block and the wedge is . The wedge is now pulled horizontally with an acceleration , as shown in the figure. Then, the minimum magnitude of for the friction between the block and the wedge to be zero, is
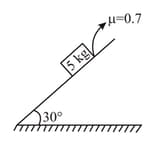
The magnitude of frictional force acting between the block and the inclined plane, as shown in the figure, is (take )
For a truck with tyres, only rear wheels are power driven and can produce acceleration. These wheels support half the entire load. If the coefficient of friction between road and each tyre is , the maximum attainable acceleration by this truck would be (Acceleration due to gravity )
Sand is to be piled up on a horizontal ground in the form of a regular cone of a fixed base of radius . Coefficient of static friction between the sand layers is . Maximum volume of the sand that can be piled up in the form of cone without slipping on the ground is
`An object of is in the state of limiting equilibrium on an inclined plane having angle of inclination Now if the angle of inclination is increased to then the extra force along the plane to be applied on the object, to keep it in equilibrium will be (take )
Find the minimum value of so that the block do not move :-
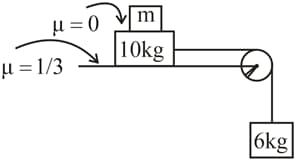
Find the acceleration of body as shown in figure. If friction is present between only and applied force is less than limiting friction.
For next three question please follow the same
An engineer is designing a conveyor system for loading lay bales into a wagon. Each bale is 0.25 m wide, 0.50 m high, and 0.80 m long (the dimension perpendicular to the plane of the figure), with mass 30.0 kg. The center of gravity of each bale is at its geometrical center. The coefficient of static friction between a bale and the conveyor belt is 0.60, and the belt moves with constant speed. The angle of the conveyor is slowly increased. At some critical angle a bale will tip (if it doesn't slip first), and at some different critical angle it will slip (if it doesn't tip first).
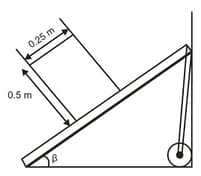
Find the second critical angle (in the same conditions) at which it slips.
If the coefficient of friction between A and B is , the maximum acceleration of the wedge A for which В will remain at rest with respect to the wedge is
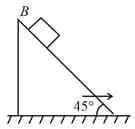
Three blocks are kept as shown in figure. Acceleration of block with respect to ground is