Gravitational Potential and Potential Energy
Gravitational Potential and Potential Energy: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Gravitational Potential Energy, Field Strength and Potentials, Gravitational Potential, Gravitational Field and Potential of a Solid Sphere, Gravitational Self Energy for Solid Sphere, etc.
Important Questions on Gravitational Potential and Potential Energy
The escape velocity for a planet is . A tunnel is dug along a diameter of the planet and a small body is dropped into it at the surface. When the body reaches the centre of the planet, its speed will be
A thin spherical shell of total mass and radius is held fixed. There is a small hole in the shell. A particle of mass is released from rest at a distance from the hole as shown. This particle subsequently moves under gravitational force of the shell. How long does it take to travel from the hole to the point diametrically opposite?
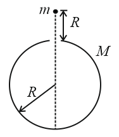
The graph shows the variation with distance of the gravitational potential (in tera joule per kilogram) due to a plane of radius .
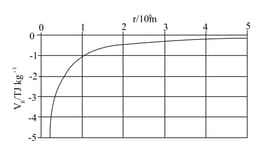
The graph shows the variation with distance of the gravitational potential (in tera joule per kilogram) due to a plane of radius .
Calculate the mass of the planet.
A particle of mass is rotating in a circular orbit of radius under the action of gravity in the presence of another stationary particle of very large mass . Consider that the gravitational potential energy is zero at infinite separation. If the total energy of the rotating particle is then, which the following expression correctly represent the angular momentum of the particle?
A body of mass is placed on the earth's surface. It is taken from the earth's surface to a height when is the radius of the earth. The change in gravitational potential energy of the body is
What is intensity of gravitational field at the centre of a spherical shell -
Three masses and are arranged in two triangular configurations as shown in figure and figure . Work done by an external agent in changing the configuration from figure to figure is

Work done by the gravitational force to bring mass from height from earth's surface to earth's surface slowly is is radius of earth
A body of mass is lifted up from the surface of earth to a height three times the radius of the earth. The change in potential energy of the body is
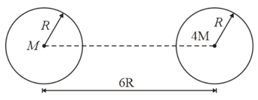
Two uniform solid spheres of equal radii but mass and have a centre to centre separation as shown in the figure. A projectile of mass is projected from the surface of the sphere of mass directly towards the centre of the second sphere. The minimum speed of the projectile so that it reaches the surface of the second sphere is
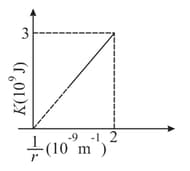
A graph of kinetic energy of an asteroid versus (where is the distance from the centre of the planet ) is shown in the figure. Asteroid falls directly towards the centre of the planet . What is the value of mass of the asteroid? ( is the mass of planet is universal gravitational constant in SI units)
Two planets have the same mass, . Each planet has a constant density, but the density of planet is twice as high as that of planet . Identical objects of mass are placed on the surfaces of the planets. What is the relationship of the gravitational potential energy, on planet 1 to on planet ?
The gravitational potential difference between a point on the surface of the planet and another point above is . Considering gravitational field to be uniform, how much work is done in moving a mass of from the surface to a point above the surface?
What is the gravitational potential on the surface of a uniform spherical shell of radius and mass if a particle of mass is placed at the centre of the sphere?
Two spheres each of mass and radius are separated by a distance of .If a line is joined in between the centres of the spheres, The gravitational potential at the midpoint of that line is
If a ball bounces to of its original height each time, then the fraction of its potential energy lost in each bounce is given by
Find the work done by the force of gravity during the upward journey when a particle of mass is thrown vertically upwards with a speed of .
There is a spherical shell of Radius R and mass M, body of mass m is placed at the centre of the spherical shell. The gravitational potential on the surface of the shell is
Distance between the centres of two stars is . The masses of two stars are and and their radii and , respectively. A body of mass is fired straight from the surface of the larger star towards the smaller star. Find the minimum initial speed by which the body is projected to reach the surface of the smaller star.
