Newton's Law of Gravitation
Newton's Law of Gravitation: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Gravitational Force, Newton's Law of Gravitation, Gravitational Force and Weight, Superposition in Gravitational Forces, Limitations of Newton's Law of Gravitation, and Properties of Gravitational Force.
Important Questions on Newton's Law of Gravitation
Two point masses of mass and , respectively, separated by distance are revolving under mutual force of attraction. The ratio of their kinetic energies will be
A mass is at the centre of a square, with four masses at the corners as shown:
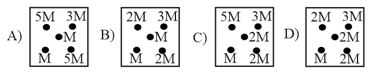
Rank the choice according to the magnitude of the gravitational force of the center mass.
A satellite is launched in the equatorial plane in such a way that it can transmit signals up to latitude on the earth. The angular velocity of the satellite is . Find .
_____ (Air Resistance/Gravitational/Natural) force is the source of centripetal force that a planet requires revolving around the Sun.
Which of Kepler's Laws of planetary motion led Newton to establish the inverse-square rule for the gravitational force between two bodies?
The centripetal force acting on a satellite revolving around the earth is . The gravitational force on that planet is also . The resultant force on the satellite is
Derive the inverse relation of the gravitational force between two bodies using Kepler's law.
The ratio of electrostatic force and gravitational force between a proton and an electron is
If the distance between two masses is doubled, the gravitational attraction between them is..
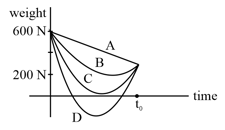
Suppose the acceleration due to gravity at the Earth's surface is and at the surface of Mars it is . A passenger goes from the Earth to Mars in a spaceship moving with a constant velocity. Neglect all other objects in the sky. Which part of the given figure best represents the weight (net gravitational force of the passenger) as a function of time?
The ratio of magnitude of electrostatic force and gravitational force acting between an electron and a proton is
A star of mass and radius is made up of gases. The average gravitational pressure compressing the star due to gravitational pull of the gases making up the star depends on as
In Cavendish's experiment why lead ball was used?
Experimentally the value of universal gravitational constant was measured by
The magnitude of the gravitational force experienced by a small spaceship of mass inside an inter-galactic dust cloud (assumed to be spherically symmetric but not necessarily uniform) when it is at a distance of from the center of the cloud is found to be
The density of the dust cloud is ( is Newton's gravitational constant)
A body weighs on the surface of the earth. How much will it weigh half way down to the centre of the earth?
Two stars of masses and are part of a binary star system. The radii of their orbits are and respectively, measured from the centre of mass of the system. The magnitude of gravitational force exerts on is
Two identical spheres each of mass and radius are separated by a distance . The gravitational force on mass placed at the midpoint of the line joining the centres of the spheres is
An astronaut of mass is working on a satellite orbiting the earth at a distance from the earth's surface. The radius of the earth is , while its mass is . The gravitational pull on the astronaut is
