Motion in a Straight Line
Motion in a Straight Line: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Basic Definitions of Motion, Motion and Rest, Reference Frames, Position of Body, Displacement of Body, Distance as Path Length, Average Velocity, Instantaneous Velocity, Average Speed, Average Acceleration, etc.
Important Questions on Motion in a Straight Line
An object moving with uniform acceleration has a velocity of in the positive direction when its coordinate is . If its coordinates later is , what is its acceleration?
At a distance from the traffic light brakes are applied to a locomotive moving at a velocity . Determine the position of the locomotive relative to the traffic light minute after the application of the brakes if its acceleration is .
A body starts from rest, what is the ratio of the distances traveled by the body during the 4th and 3rd seconds?
A body dropped from top of a tower falls 40 m during the last two seconds of its fall. The height of tower is
A car moves a distance of 200 m. It covers the first half of the distance at speed and the second half of distance at speed v. The average speed is . Find the value of v
A bus travelling the first one third distance at a speed of , the next one third at and the last one – third at . The average speed of the bus is
A particle covers half of its total distance with speed and the rest half distance with speed . Its average speed during the complete journey is
A body is moving with velocity towards east. After 10 seconds its velocity becomes towards north. The average acceleration of the body is
A car covers the first half of the distance between two places at and other half at . The average speed of the car is
A particle moves a distance x in time t according to equation The acceleration of particle is proportional to:
A particle has initial velocity and has acceleration Its speed after 10 s is:
A ball is dropped from a high rise platform at, starting from rest. After another ball is thrown downwards from the same platform with the speed . The two balls meet at, . What is the value of ? (Take, )
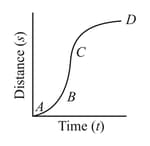
A particle shows distance–time curve as given in this figure. The maximum instantaneous velocity of the particle is around the point:
A car moves from X to Y with a uniform speed and returns to X with a uniform speed . The average speed for this round trip is
What will be the ratio of the distances moved by a freely falling body from rest in fourth and fifth seconds of the journey?
The position of a particle with respect to time along -axis is given by, where, is in meters and is in seconds. What will be the position of this particle when it achieves maximum speed along the direction?
Two bodies, (of mass ) and (of mass ), are dropped from heights of and , respectively. The ratio of the times taken by them to reach the ground is
A ball is thrown vertically upwards. It has a speed of when it has reached one half of its maximum height. How high does the ball rise?
(Take, )
If a ball is thrown vertically upwards with speed u, the distance covered during the last t seconds of its ascent is
A car moving with a speed of can be stopped by applying brakes at least after . If the same car is moving with a speed of , what is the minimum stopping distance?
