Inertial and Non-inertial Frames of Reference
Inertial and Non-inertial Frames of Reference: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as inertial frame of reference, non-inertial frame of reference, and limitations of Newton's laws of motion.
Important Questions on Inertial and Non-inertial Frames of Reference
A reference frame attached to the earth
A lift is moving down with acceleration a. A man in the lift drops a ball inside the lift. The acceleration of the ball as observed by the man in the lift and a man standing stationary on the ground are respectively –
In which of the following cases does Newton's second law is not applicable?
Newton's laws are not applicable when
(1) Observation is done via inertial frame of reference
(2) Observation is done via non-inertial frame of reference
(3) Object is travelling with a speed comparable to the speed of light
Are there limitations to Newton’s third law? Why?
Give two examples of non-inertial frame of reference.
Newton's law of motion is applicable in non-inertial frame of reference.
What acceleration should the table be moved so that the block first freely initially?
Assertion: In the reference frame of centre of mass, net force acting on system is always zero.
Reason: A pseudo force given by (where is mass of system and is acceleration of centre of mass) acts on system which balances all the external forces.
Assertion: An observer moving with constant speed must be an inertial reference frame.
Reason: An observer is called inertial if its change in velocity is zero.
A block of mass is attached to a spring in natural length of spring constant . The other end of the spring is moved with a constant velocity away from the block. Find the maximum extension in the spring.

A reference frame attached to the Earth
A bird is sitting in a large closed cage which is placed on a spring balance. It records a weight of 5N. The bird of mass 0.5 kg files upward in the cage with an acceleration of . The spring balance will now record a weight of......... at that moment?
A physics professor in his car drops a coffee mug while moving at a constant velocity of along the highway. The professor notices that it only takes a half a second for the mug to drop straight down to the floor of his car. A student standing alongside the road sees the mug moving in a parabola with respect to her. What time does she measure for the mug to hit the floor of the car?
Two observers are situated in different inertial reference frames. Then,
For ordinary terrestrial experiments, the observer in an inertial frame in the following cases is
Observer is in a lift accelerating upwards and is on the ground. Both apply Newton's law, and measure normal reaction on the body
Consider two observers moving with respect to each other at a speed along a straight line. They observe a block of mass moving over a distance on a rough surface. The following quantities will be same as observed by the two observers
A circular disc with a groove along its diameter is
placed horizontally. A block of mass is placed as shown. The coefficient of friction between the block and all surfaces of groove in contact is .
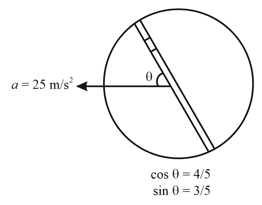
The disc has an acceleration of . Find the acceleration of the block with respect to disc,
Inside a horizontally moving box, an experimenter finds that when an object is placed on a smooth horizontal table and is released, it moves with an acceleration of . In this box if body is suspended with a light string. the tension in the string in equilibrium position.(w.r.t. experimenter) will be (Take )
