Inertial and Non-inertial Frames of Reference
Inertial and Non-inertial Frames of Reference: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Frame of Reference, Inertial Frame of Reference, Non-inertial Frame of Reference, Pseudo Force, Motion in Accelerating Frame, and Pseudo Force in Linearly Accelerated Frames.
Important Questions on Inertial and Non-inertial Frames of Reference
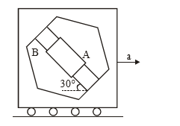
A circular disc with a groove along its diameter is placed horizontally on a rough surface. A block of mass is placed as shown. The co-efficient of friction between the block and all surfaces of groove and horizontal surface in contact is The disc has an acceleration of towards left. Find the acceleration of the block with respect to disc. Given,
Two blocks of mass and , connected to each other by a massless inextensible string of length are placed along a diameter of a turn table. The coefficient of friction between the table and is while there is no friction between and the table. The table is rotating with an angular velocity of about a vertical axis passing through its centre . The masses are placed along the diameter of the table on either side of the centre such that the mass is at a distance of from . The masses are observed to be at rest with respect to an observer on the turn table. Calculate the frictional force on .
A reference frame attached to the earth
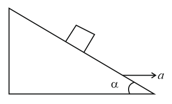
A block is kept on a frictionless inclined surface with angle of inclination . The incline is given an acceleration to keep the block stationary. Then is equal to –
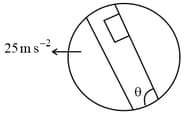
A lift is moving down with acceleration a. A man in the lift drops a ball inside the lift. The acceleration of the ball as observed by the man in the lift and a man standing stationary on the ground are respectively –
A spring balance is attached to the ceiling of a lift. A man hangs his bag on the spring and the spring reads , when the lift is stationary. If the lift moves downward with an acceleration of , the reading of the spring balance will be –
A piece of wire is bent in the shape of a parabola (-axis vertical) with a bead of mass on it. The bead can slide on the wire without friction. It stays at lowest point of the parabola when the wire is at rest. The wire is now accelerated parallel to the -axis with a constant acceleration . The distance of the new equilibrium position of the bead, where the bead can stay at rest with respect to the wire, from the -axis is
A rocket is fired vertically from the earth with an acceleration of 2g, where g is the gravitational acceleration. On an inclined plane inside the rocket, making an angle with the horizontal, a point object of mass m is kept. The minimum coefficient of friction between the mass and the inclined surface such that the mass does not move is:
Inside a horizontally moving box, an experimenter finds that when an object is placed on a smooth horizontal table and is released, it moves with an acceleration of . In this box, if body is suspended with a light string, the tension in the string in equilibrium position (with respect to experimenter) will be (Take )
The collar is free to slide along the frictionless and plane rod mounted in the frame. What would be the acceleration of the frame in horizontal direction required to maintain the collar in stationary position on the shaft.
A boy is in a lift which is moving downwards with an acceleration . At an instant when the velocity of the lift is , then boy throws a ball upwards with a velocity . The time in after which the ball will return into the hand of boy is
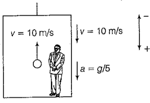
In figure a sphere of mass is suspended from the ceiling of a car which is initially at rest. Tension in the string in this situation is The car now moves to right with a uniform acceleration and the tension in the string is now then
A boy sitting on the topmost berth in the compartment of a train which is just going to stop on a railway station, drops an apple aiming
at the open hand of his brother sitting vertically below his hands at a distance of about meter. The apple will fall
Give two examples of non-inertial frame of reference.
Newton's law of motion is applicable in non-inertial frame of reference.
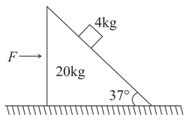
All surfaces shown in the figure are frictionless. A block of mass is kept on a wedge of mass The magnitude of force required so that the block remains stationary w.r.t. wedge, is
A girl drops an apple from the window of a train which is moving on a straight track with speed increasing with a constant rate. The trajectory of the falling apple as seen by the girl is
A cabin is moving vertically upwards with an acceleration A massless string is attached to the ceiling of the cabin on which a bead of mass is sliding downwards with respect to string with an acceleration The tension in the string is
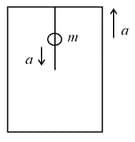
A body of mass is placed inside a lift as shown in figure. Lift start accelerating with acceleration a in upward direction. If lift start
moving from rest, then the work done by normal reaction, in the ground frame of reference, in time is
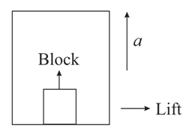
A box is kept in the rear of a truck that is travelling on a level road. The coefficient of sliding friction between box and truck bed is . The driver suddenly applies the brakes, producing a deceleration . Acceleration of box with respect to truck is: