Newton's Second Law of Motion
Newton's Second Law of Motion: Overview
This topic contains concepts like Mass, Units of Mass, Linear Momentum, and Change of Momentum.
Important Questions on Newton's Second Law of Motion
A lift weighing is moving upwards with an acceleration of . The tension in the supporting cable is
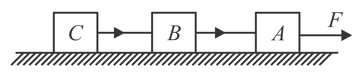
Three identical blocks of masses are drawn by a force on a frictionless surface, then what is the tension (in ) in the string between the blocks and ?
How the mass of a body can be defined using newton's second law of motion?
The weight of a body depends on its mass but, the mass of the body does not depend on its weight.
Explain weight and how it is different from mass?
What is the concept of mass? What is difference between inertial and gravitational mass ?
Evaluate the Direction & Magnitude of the Net Force of a Stone of Mass 6 Kg Falling Out of the Window of a Stationary Bus.
The application of force on an object may change its _____.
What is a simple definition of force?
Is force a vector quantity True or false?
Resultant force is the _____ (scalar/vector) sum of the all the force acting on the object.
The momentum of a system of particles is always conserved. True or false?
A constant retarding force of is applied to a body of mass moving initially with a speed of . How long does the body take to stop?
A body under the action of a force acquires an acceleration of . The mass of the body is _____ .
Name the quantity which is obtained by dividing change of momentum with time.
Assign a single name to the rate of change of momentum.
If external force on a body is zero, its
A body is moving under the action of two forces . For its velocity to become uniform a third force acts on it, then this force can be given by:
A body of mass starts from the origin with an initial velocity . If a constant force acts on the body, the time at which the -component of the velocity becomes zero is
