Newton’s Laws of Motion
Newton’s Laws of Motion: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Aristotle Fallacy, Newton's Second Law of Motion, Constraint Equation in Inclined Planes & Constraint Equation in Wedges etc.
Important Questions on Newton’s Laws of Motion
Physical independence of force is a consequence of,
A block of mass m is placed on a smooth wedge of inclination The whole system is accelerated horizontally so that the block does not slip on the wedge. The force exerted by the wedge on the block (g is acceleration due to gravity) will be
A block of mass is placed on a smooth wedge of inclination . The whole system is accelerated horizontally so that the block does not slip on the wedge. The force exerted by the wedge on the block ( is acceleration due to gravity) will be
The coefficient of static friction, , between block of mass and the table as shown in the figure is . What would be the maximum mass value of block so that, the two blocks do not move? The string and the pulley are assumed to be smooth and massless .
A body of mass 5 kg explodes at rest into three fragments with masses in the ratio 1 : 1 : 3. The fragment with equal masses fly in mutually perpendicular directions with speeds of 21 ms-1. The velocity of heaviest fragment in ms-1 will be
A monkey of mass is holding a vertical rope. The rope will not break when a mass of is suspended from it but will break if the mass exceeds . What is the maximum acceleration with which the monkey can climb up along the rope?
A man weighing 80 kg, stands on a weighing scale in a lift which is moving upwards with a uniform acceleration of What would be the reading on the scale?
A lift weighing is moving upwards with an acceleration of . The tension in the supporting cable is
If a cricketer catches a ball of mass moving with a velocity of , then he experiences a force of (Time taken to complete the catch is )
A block has been placed on an inclined plane with the slope angle block slides down the plane at constant speed. The coefficient of kinetic friction is equal to :
A monkey is descending from the branch of a tree with constant acceleration. If the breaking strength is 75% of the weight of the monkey, the minimum acceleration with which monkey can slide down without breaking the branch is
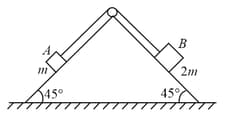
Block of mass and block of mass are placed on a fixed triangular wedge by means of a massless inextensible string and a frictionless pulley as shown in figure. The wedge is inclined at to the horizontal on both sides. The coefficient of friction between block and the wedge is and that between block and the wedge is . If the system of and is released from rest, find the magnitude and direction of the force of friction acting on
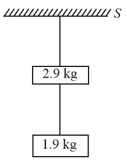
Two blocks of mass and are suspended from a rigid support by two inextensible wires each of length see figure. The upper wire has negligible mass and the lower wire has a uniform mass of . The whole system of blocks, wires and support has an upward acceleration of . Acceleration due to gravity is .
(i) Find the tension at the mid-point of the lower wire.
(ii) Find the tension at the mid-point of the upper wire.
Two cubes of masses and be on two frictionless slopes of block A which rests on a horizontal table. The cubes are connected by a string which passes over a pulley as shown in the figure. To what horizontal acceleration f should the whole system (that is the blocks and cubes) be subjected so that the cubes do not slide down the planes? What is the tension of the string in this situation?
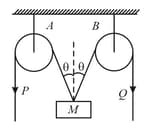
In the arrangement shown in the figure, the points and of the two inextensible strings move downwards with uniform speed . If the pulleys and are fixed, then the mass moves upwards with a speed
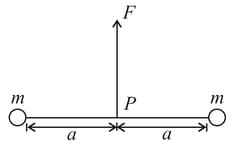
Two particles of mass each are tied at the ends of a light string of length The whole system is kept on a frictionless horizontal surface with the string held tight so that each mass is at a distance from the centre (as shown in the figure). Now, the mid-point of the string is pulled vertically upwards with a small but constant force As a result, the particles move towards each other on the surface. The magnitude of acceleration, when the separation between them becomes is
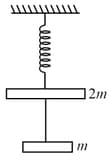
The string between blocks of mass and is massless and inextensible. The system is suspended by a massless spring as shown. If the string is cut find the magnitudes of accelerations of mass and (immediately after cutting)
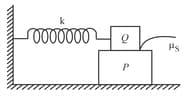
A block of mass is placed on a horizontal frictionless plane. A second block of mass is placed on it and is connected to a spring of spring constant the two blocks are pulled by distance . Block oscillates without slipping. What is the maximum value of frictional force between the two blocks?
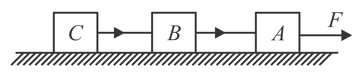
Three identical blocks of masses are drawn by a force on a frictionless surface, then what is the tension (in ) in the string between the blocks and ?
A light string passing over a smooth light pulley connects two blocks of masses m1 and m2 (vertically). If the acceleration of the system is , then the ratio of the masses is –