Stable, Unstable and Neutral Equilibrium
Stable, Unstable and Neutral Equilibrium: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Lami's Theorem, Stable Equilibrium, Equilibrium of Forces, Neutral Equilibrium, Unstable Equilibrium, Equilibrium of Bodies and, Application of Lami's Theorem
Important Questions on Stable, Unstable and Neutral Equilibrium
A block of mass is placed on a smooth wedge of inclination . The whole system is accelerated horizontally so that the block does not slip on the wedge. The force exerted by the wedge on the block ( is acceleration due to gravity) will be
Two cubes of masses and be on two frictionless slopes of block A which rests on a horizontal table. The cubes are connected by a string which passes over a pulley as shown in the figure. To what horizontal acceleration f should the whole system (that is the blocks and cubes) be subjected so that the cubes do not slide down the planes? What is the tension of the string in this situation?
Differentiate between stable, unstable and neutral equilibrium.
The potential energy of a particle as function of position is given by, where is in metre. The equilibrium position of the particle will be
If . The angle between and and are and , respectively. Then, the magnitude of vectors and are in ratio of :
Two rods and are attached to a weight of mass as shown in figure, then:
What is equilibrium force in physics? Elaborate with an example the equilibrium of force?
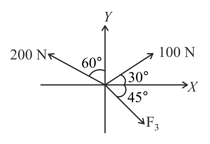
If resultant of these three forces is along -axis, then is equal to:
A uniform body of length is carried by a father and a son by keeping the ends on their shoulders. If the son carries only one fourth the load carried by the father, find the position of the centre of gravity.
A uniform meter scale has a mass of . Masses of and are suspended from its end. At what points must the rod be supported so that it may remain horizontally in equilibrium.
A man weighing walk along a rope tied between two pegs which are apart horizontally. When he comes to the middle point of the rope it sags by . Calculate the tension in the string.
A body of mass is suspended by two strings of length and attached to two points apart in the same horizontal line. Find the tensions in the strings.
A mass of is placed at one end of a uniform metre scale. The scale balances in a knife edge at a point from the end. Find the weight of the metre scale.
A uniform plank long weighing rests symmetrically as two knife edges one metre apart from each other. If a mass of be hung at one end of the plank and a mass of at the other end, find the reactions on the knife edges.
Give an example of a body in equilibrium but not at rest.
Can a body be in equilibrium, if it is in motion? Explain.
What are the conditions for two colinear forces to be in equilibrium?
Can a body be in equilibrium, even if only one external force acts on it? Explain.
Will a car be in equilibrium while taking a U-turn?
Pick the CORRECT option/options.
