Nature of Physical Laws
Nature of Physical Laws: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Nature of Physical Laws, Conservation Laws, Conservation of Energy, Conservation of Momentum, Conservation of Angular Momentum & Conservation of Charge etc.
Important Questions on Nature of Physical Laws
A ball of mass 5kg moving at 3m/s collides with another ball of mass 3kg moving at 5m/s in the same direction. If the balls move together after the collision in the same direction, find their common velocity.
Rockets work on the principle of conservation of _____
The law of conservation of energy is applicable to mechanical systems as they require energy input to keep working
CV Raman discovered that when light traverses a transparent material, some of the deflected light changes in _____.
The field particle of the nuclear forces are:
In a particle accelerator, a current of is carried by a proton beam in which each proton has a speed of . The cross-sectional area of the beam is The charge density in this beam is close to
A train is moving slowly at next to a railway platform. A man, tall, alights from the train such that his feet are fixed on the ground. Taking him to be a rigid body, the instantaneous angular velocity (in ) is
In a particle accelerator, a current of is carried by a proton beam in which each proton has a speed of . The cross-sectional area of the beam is The charge density in this beam (in is close to
A person holds two metal spheres in his hands and stands on a rotating table. What can you say about the angular velocity of that person if he brings his hands near his chest?
A thin uniforrm circular ring of mass and radius is rotating about its axis with a constant angular velocity . Two particles each of mass $\mathrm{m}$, are attached gently to the opposite ends of a diameter of the ring. The ring now rotates with new angular velocity
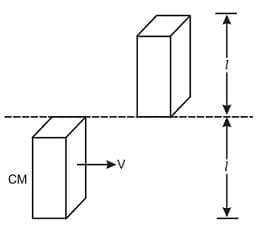
A bar of mass m length l is in pure translatory motion with its centre of mass moving with velocity v. It collides with another identical bar at rest and sticks to it as shown in diagram. Assuming that after collision it becomes one composite bar of length 2l, calculate the angular velocity of the composite bar -
A ring of radius , made of a highly dense material, has a mass , distributed uniformly over its circumference. A highly dense particle of mass is placed on the axis of the ring, at a distance from the center of the ring. Find the speed of the particle (in ), when the particle is at the center of the ring. Except for mutual gravitational interaction between the two, neglect all other forces.
A projectile of mass is fired from the surface of the earth at an angle from the vertical. The initial speed of the projectile is , where and are mass and the radius of the earth. Find the maximum height attained by the projectile in . Neglect air resistance and the rotation of the earth. (Given: .)
Bernoulli’s theorem is nothing but a statement of conservation of _____ for liquids.
Charge can neither be created nor destroyed.
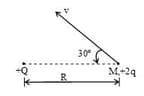
In the diagram shown, the charge is fixed. Another charge , is projected from a distance from the fixed charge. Minimum separation between two charges if the velocity becomes times of the projected velocity at this moment is (assume gravity to be present) in cm ( given)
A ball of radius has a mass and moment of inertia about its diameter . The ball rolls without slipping over a rough horizontal floor with velocity towards a smooth vertical wall. If the coefficient of restitution between the wall and ball is then the velocity of the ball in after long time after collision is
A disc is rotating freely about its axis. Percentage change in angular velocity of disc if temperature decreases by is (coefficient of linear expansion of material of disc is )
Two identical discs are positioned on a vertical axis. The bottom disc is rotating with angular velocity . The top disc is initially at rest. It is allowed to fall and sticks to the lower disc. Ratio of before and after collision.
A bomb at rest explodes into three parts of the same mass. The linear momentum of two parts are and . The magnitude of momentum of third part is . Find .