Conditions of Equilibrium
Conditions of Equilibrium: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Stable Equilibrium, Unstable Equilibrium, Neutral Equilibrium, Equilibrium of Rigid Body, Translational Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies & Rotational Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies etc.
Important Questions on Conditions of Equilibrium
If potential energy function for the force between two atoms in a diatomic molecule is approximately given by , where and are constants in standard SI units and is in metres. Find the dissociation energy of the molecule (in ). [Take and ]
A system is said to be in static equilibrium when, net force acting on the body is zero, net _____ acting the block is zero and velocity of the block is also zero.
If three coplanar forces keep a body in equilibrium, then they are always concurrent.
A body is acted upon by two unequal forces in opposite directions, but not in the same line. The effect is that
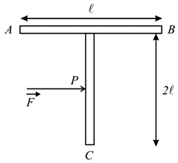
A shaped object with dimensions shown In the figure, is lying on a smooth floor. A force is applied at the point parallel to such that the object has only the translational motion without rotation. Find the location of with respect to
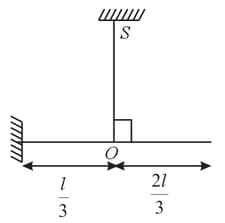
A rod of mass and length is suspended from a vertical wall and kept horizontal by a massless vertical thread as shown. The tension in the thread is,
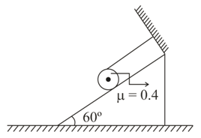
A solid cylinder of mass is wrapped with a string and placed on a rough inclined plane as shown in the fig. Then the frictional force acting between cylinder and plane is
A rectangle block rests on a horizontal table. A horizontal force is applied on the block at a height above the table to move the block. Does the line of action of the normal force exerted by the table on the block depend on ?
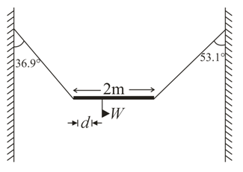
A non-uniform bar of weight is suspended at rest by two strings of negligible weight as shown in Fig. The angles made by the strings with the vertical are and respectively. The bar is long. Calculate the distance of the centre of gravity of the bar from its left end.
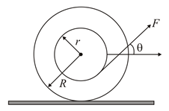
A spool is pulled at an angle with the horizontal on a rough horizontal surface as shown in the figure. If the spool remains at rest, the angle is equal to
A thin uniform rod of mass m and length is moving translationally with acceleration due to two antiparallel forces, as shown. One of the forces is . Find the maximum value of acceleration for which rod may move translationally.
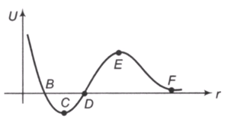
The given plot shows the variation of , the potential energy of interaction between two particles with the distance separating them .
1. and are equilibrium points
2. is a point of stable equilibrium
3. The force of interaction between the two particles is attractive between points and and repulsive between and
4. The force of interaction between particles is repulsive between points and .
Which of the above statements is correct?
represents the potential energy between two atoms in a molecule, where is the distance between the atoms and and are positive. The atom will be in stable equilibrium if
A particle of mass lying on axis experiences a force given by law, , where is the coordinate of the particle in .
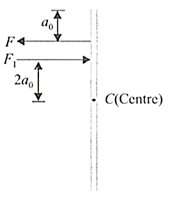
A horizontal force is applied to on the block as shown, which makes it to move with a constant velocity. The coefficient of friction between the block and the surface is . is applied at height from ground . Distance is the horizontal distance between a point on the bottom face of the block at which the resultant of the friction and normal force act and CG of the block. Find .
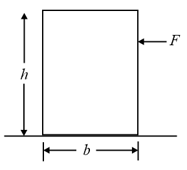
The front wall of a drawer in a cabinet is a provided with two symmetrical handles. The distance between the handles is and the length (i.e. depth) of the drawer is . The maximum value of the coefficient of friction between drawer and cabinet, for which drawer can be pulled out by applying a force on one handle perpendicular to the face of the drawer is: (Neglect the weight of the drawer)
If potential energy function for the force between two atoms in a diatomic molecule is approximately given by , where and are constants in standard SI units and is in metres. Find the dissociation energy of the molecule (in ). [Take and ]
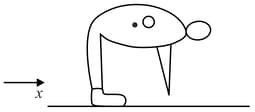
Consider an obese person bent forward on the ground whose center of mass is at O. The person's hands don't touch the ground. Then friction on the shoes
An object placed on a ground is in stable equilibrium. If the objects is given a slight push, then initially the position of centre of gravity
If a man having bag in his hand moves up on a stair. Then